
Originally set to expire on June 30, 2021, the Oncology Care Model was extended for an additional year in light of the COVID-19 pandemic.

Maggie is a senior editor for The American Journal of Managed Care® (AJMC®) and produces written, video, and podcast content covering several disease states. She joined AJMC® in 2019, and has been with AJMC®’s parent company, MJH Life Sciences®, since 2014, when she started as a copy editor.
She has a BA in English from Penn State University. You can connect with Maggie on LinkedIn.

Originally set to expire on June 30, 2021, the Oncology Care Model was extended for an additional year in light of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Research that will be presented at Heart Failure 2021 shows patients with heart failure may have a greater incidence of several types of cancer and that this chance is even higher in women vs men.

The Supreme Court recently upheld the Affordable Care Act, under which HIV and AIDS are considered preexisting conditions, by a vote of 7 to 2.
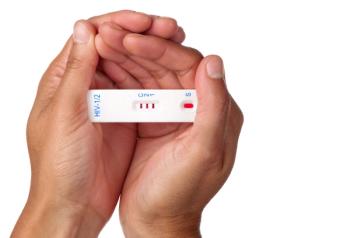
Despite gains in HIV testing rates among individuals 13 years and older, total testing rates remain at suboptimal levels among both commercial insurance and Medicaid beneficiaries.

Survey responses from the San Francisco Bay Area, from men who have sex with men (MSM), show differing behavioral and social influences on the risk of sexually transmitted infections (STIs).

Early intensive treatment was more efficacious at slowing disease accumulation in patients with relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis (RRMS) vs initiating therapy with a moderate-efficacy disease-modifying treatment (DMT) prior to switching to a higher-efficacy DMT.

As a specialized health care service, telemedicine was shown to be comparable to traditional care for persons living with HIV in rural Georgia.

Compared with individuals without known HIV infection, persons living with HIV had higher rates of sudden cardiac death and increased interstitial myocardial fibrosis in a new New England Journal of Medicine study.

Out-of-pocket (OOP) spending for patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction rose in the event of a worsening heart failure event across the 4 phases of Medicare Part D coverage.

The study authors hope their findings inform future interventions whose goal is to minimize the comorbidity burden of adults with multiple sclerosis (MS), thereby improving their quality of life and ultimate health outcomes.

Results from 2 studies presented at this year’s European Hematology Association meeting demonstrate the long-term tolerability and efficacy of the Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitor.

Compared with their peers receiving injectable treatments for their relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis (RRMS), children who received newer disease-modifying therapies (DMTs) had improved scores on several measures of disease progression.

Progressive rehabilitation produced superior results among patients randomized to a 36-session program during or following hospitalization for acute decompensated heart failure vs those randomized to usual care.

This week marks the 40th anniversary of the CDC's June 5, 1981, Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report describing rare instances of immunocompromised status among 5 homosexual men in Los Angeles. The American Journal of Managed Care® spoke recently with lead author Michael Gottlieb, MD, who was the first to describe what would come to be known as HIV and AIDS.

Data from the DAPA-HF trial and published literature show intermediate-level cost-effectiveness of dapagliflozin use among patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF).
Here are some of the latest developments in multiple sclerosis (MS) from our sister publication, NeurologyLive®.

Between 2014 and 2018, annual diagnoses for HIV in an emergency department (ED) in Hamilton County, Ohio, more than doubled, from 20 to 42.
Mount Sinai research released today shows a possible link between excess pericardial fat and greater risk of heart failure, with implications for early intervention and prevention of heart disease.

Here is some of the latest news in diabetes from our sister publication Pharmacy Times®.

The latest coverage in the heart failure space from across MJH Life Sciences™.

Here are some of the latest developments in multiple sclerosis (MS) from our sister publication, NeurologyLive®.

May 18 is HIV Vaccine Awareness Day. Here we explore just a few of the many reasons why a vaccine that is effective at preventing the acquisition of HIV and at reducing the viral load in those currently living with HIV remains an elusive goal.

Rates of acute heart failure (AHF) have recently been rapidly increasing among elderly and super-elderly patients in Japan, and this study investigated rates of all-cause death and mode of death among this patient population.

These 4 studies were pegged as “ones to watch” during the American College of Cardiology (ACC) annual briefing on results for consumers. They will be presented in the opening session of late-breaking clinical trial results on day 1 of ACC.21.

Although knowledge is plentiful on disease state improvements for adult patients with multiple sclerosis (MS) following use of newer disease-modifying therapies, less is known about similar outcomes among patients with pediatric-onset MS (POMS).

Despite overall survival improvements among pediatric patients living with HIV, 20.5% are still lost to follow-up.

Compared with nonsmokers who did not have recent exposure to secondhand smoke, a 35% greater chance for heart failure was seen among those with recent exposure to the toxic fumes.
New research demonstrates that patients with multiple sclerosis (MS) who were asymptomatic for COVID-19 had lower antibody levels against SARS-CoV-2, its causative virus, due to having fewer B cells.

Because real-world data are lacking on disease-modifying treatment (DMT) prescribing patterns for patients with multiple sclerosis (MS), a team of investigators wanted to make sure these individuals were receiving adequate care.

Disproportionate rates of HIV and sexually transmitted infections (STIs) among Black women, who have a nearly 4 times higher enrollment rate in community supervision programs, underscores the need for culturally targeted HIV/STI interventions.

259 Prospect Plains Rd, Bldg H
Cranbury, NJ 08512
© 2025 MJH Life Sciences®
All rights reserved.
