Allergy
Latest News
Latest Videos

CME Content
More News
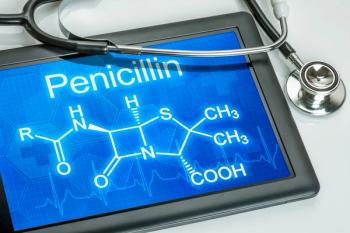
EHR penicillin allergy flags do not often match allergist assessments, highlighting the need for improved evaluation processes.

Acute exacerbations of chronic rhinosinusitis are poorly defined and often overtreated, calling for standardized diagnostic criteria and more evidence-based management.

Explore the latest breakthroughs in allergy treatments, including FDA approvals and emerging therapies that enhance patient care and address systemic challenges.

Chronic inducible cold urticaria is rare, but a new study suggests it can have significant impacts on patients’ daily lives.

A new study links immune markers and coping patterns to disease control in adolescents with chronic urticaria.

A recent study compares AI models DeepSeek-R1 and ChatGPT-4o in providing accurate, accessible information on urticaria, with DeepSeek showing superior performance.

Remibrutinib demonstrated rapid and sustained symptom relief for chronic spontaneous urticaria in a pooled analysis of REMIX-1 and REMIX-2.

Urticaria symptom reduction with remibrutinib was linked with improved quality of life and sleep for patients with chronic spontaneous urticaria.

Remibrutinib shows rapid and sustained relief for chronic spontaneous urticaria, offering a promising oral treatment option for patients.

Key factors influencing chronic urticaria duration highlight the importance of early identification and management in primary care settings.

There is a significant link between chronic spontaneous urticaria and cardiovascular disease risk, highlighting the need for routine assessments.

Combining ELR with CT-based measures predicts olfactory recovery in CRSwNP patients, highlighting eosinophils' role in disease severity and dysfunction.

Chronic spontaneous urticaria (CSU) and atopic disorders seem to share an immunological basis and may significantly benefit from type 2 inflammation–targeted therapies.

Guidelines that encouraged the exposure of peanuts in children were found to significantly reduce food allergies.

Allergen immunotherapy was associated with reduced medication use and improved asthma control for up to 9 years.

The approval of remibrutinib for patients with chronic spontaneous urticaria was supported by data from the phase 3 REMIX-1 and REMIX-2 clinical trials.
Female patients with chronic spontaneous urticaria (CSU) face greater disease severity and burdens, particularly in midlife, a study found.

Gary Falcetano, PA-C, AE-C, discussed the correlation between climate change and allergy health risks.

The chronic spontaneous urticaria treatment landscape has shifted in recent years, with expanding treatment options for patients with refractory disease.

Families reported quality of life improvements when they used peanut oral immunotherapy instead of simply avoiding peanuts.

As many as one quarter of people with chronic urticaria also have metabolic syndrome, data suggest.

Synthetic generation replicates key clinical patterns from real-world data, enabling valid analyses with fewer patients.

Identifying specific biomarkers and clinical characteristics is crucial for predicting a patient's response to both existing and emerging treatments for chronic spontaneous urticaria, thereby moving toward a more personalized approach to care.

Chronic spontaneous urticaria places a heavier burden on patients than atopic dermatitis and psoriasis, leading to a worse quality of life and higher health care costs, underscoring the critical need for better treatments.

When updated food allergy prevention guidelines were directly provided to families, they led to earlier allergen introduction in infants and significantly reduced the prevalence of IgE-mediated peanut, egg, and cow's milk allergies.