
Kassandra Munger, ScD, of the Harvard TH Chan School of Public Health, discusses findings that vitamin D deficiencies are linked to a greater risk of multiple sclerosis.

Kassandra Munger, ScD, of the Harvard TH Chan School of Public Health, discusses findings that vitamin D deficiencies are linked to a greater risk of multiple sclerosis.

The biggest difference between ocrelizumab and the recently approved ofatumumab is that ofatumumab can be taken at home for relapsing forms of multiple sclerosis (MS), explained Patricia K. Coyle, MD.
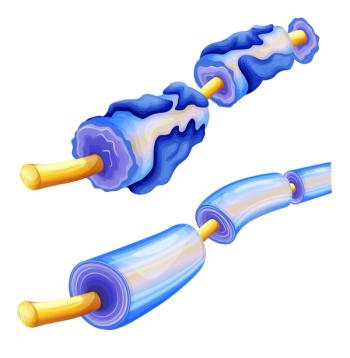
Researchers hope that a more targeted retinoid acid X receptor compound could repair myelin without the adverse effects seen in every patient in this trial, which tested an already approved cancer drug.

Disease-modifying therapies (DMTs) are primarily effective through immunomodulation, in that they target relapse prevention, said Burcu Zeydan, MD, assistant professor of neurology, assistant professor of radiology, at Mayo Clinic.

Obesity is common in the general population and research has shown it can increase the risk of multiple sclerosis (MS), as well as increase diagnostic delays, explained Ruth Ann Marrie, MD, PhD, director of the Multiple Sclerosis Clinic at the University of Manitoba.

Nurses often get involved with patients with multiple sclerosis (MS) before their diagnosis and then work to educate them on the disease and its care, said Amy Perrin Ross, APN, MSN, CNRN, MSCN, Neuroscience Program Coordinator at Loyola University Medical Center.

To the extent that some factors are modifiable, the takeaway for clinicians is to encourage their patients with multiple sclerosis (MS) to adopt healthy habits.

The drug, mastinib, reduced the chance of a confirmed disability progression by 37% in phase 2b/3 study results.

With more multiple sclerosis (MS) treatments becoming available, it is now possible to better personalize approaches, explained speakers during a session at MSVirtual 2020: 8th Joint ACTRIMS-ECTRIMS Meeting.

It is well known that women are disproportionately affected by multiple sclerosis (MS), but there remains a lack of understanding regarding gender differences in response to treatments for MS, said Riley Bove, MD, assistant professor of neurology at the UCSF Weill Institute for Neurosciences.

Do patients with multiple sclerosis who have been on disease-modifying therapies (DMTs) for decades need to keep taking them? John Corboy, MD, professor of neurology, University of Colorado Denver, School of Medicine, and co-director of the Rocky Mountain MS Center at Anschutz Medical Campus, explains what is known about this area.

Post hoc data from 2 late-stage studies about siponimod, sold as Mayzent by Novartis, illustrated improved cognitive processing speed and delayed time to disability in multiple sclerosis.

A minority of patients with multiple sclerosis (MS) have primary progressive disease, and it has few treatment options.

Many patients with secondary progressive multiple sclerosis (SPMS) are actually being misclassified and treated as if they have relapsing-remitting MS (RRMS), which can have an impact on research, treatment, and health care planning, said Jan Hillert, MD, PhD, professor and senior physician at Karolinska Institutet.
The analysis, which was released on the first day of the meeting, was one of many that tried to demonstrate that earlier treatment in newly diagnosed and younger patients may forestall disease progression and disability.

There is a push to diagnose multiple sclerosis (MS) earlier, which can lead to misdiagnosis if the diagnostic criteria aren’t used properly, explained Patricia K. Coyle, MD, director of the MS Comprehensive Care Center and professor of neurology at Stony Brook University Neurosciences Institute.

A joint session of ECTRIMS and the European Academy of Neurology assesses important topics in measuring relapse and progression in multiple sclerosis (MS).

Patients with multiple sclerosis (MS) have a generally increased risk of cardiovascular disease, and some evidence is emerging that disease-modifying treatments may alter this risk. Thomas Frisell, PhD, coordinator of the Clinical Epidemiology Unit, Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, Sweden, discusses whether newer treatments for MS, such as ozanimod, may present an improved cardiac safety profile for patients with MS versus older treatments, such as fingolimod.

Multiple sclerosis (MS) can be a challenging disease to diagnose because of its broad range of symptoms and because of the fact that many other syndromes can mimic MS. Additionally, the McDonald Criteria, which are clinical, radiographic, and laboratory criteria used for diagnosing MS, are sometimes misapplied, according to Andrew Solomon, MD, associate professor of neurological sciences and division chief of multiple sclerosis at Larner College of Medicine, The University of Vermont, Burlington, Vermont.

Results for ozanimod, which is under review by FDA and European regulators for treatment of relapsing multiple sclerosis (MS), were presented in poster sessions September 12, 2019, at ECTRIMS 2019, the 35th Annual Congress of the European Committee for Treatment and Research in Multiple Sclerosis, taking place in Stockholm, Sweden.

Age is an important factor in the disease burden of multiple sclerosis (MS), as rising age both impacts disease course and brings with it additional risk of comorbidities. However, disease duration may be an even more important factor than age in reaching disability milestones, according to Viktor von Wyl, PhD, project leader, Epidemiology, Biostatistics and Prevention Institute, University of Zurich, Zurich, Switzerland.

FDA recently accepted the Biologics Licensing Application for inebilizumab to treat a rare autoimmune condition, neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder. The results for inebilizumab were presented at the 35th Annual Congress of the European Committee for Treatment and Research in Multiple Sclerosis, taking place in Stockholm, Sweden.

While current therapies for multiple sclerosis (MS) that treat focal inflammation are beneficial for many patients, there are other crucial aspects of the disease, including brain volume loss, that are not clearly linked to this inflammation and that demand new therapeutic developments, said Jan Hillert, MD, PhD, professor and senior physician in the department of clinical neuroscience, Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, Sweden.

Speakers at a session at ECTRIMS 2019 on long-term outcomes in multiple sclerosis said that better therapies and improved understanding of the effect of comorbidities have improved outcomes. The session was part of the 35th Annual Congress of the European Committee for Treatment and Research in Multiple Sclerosis, taking place in Stockholm, Sweden.

Maria Trojano, MD, professor of neurology at the University of Bari, Italy, offered the opening lecture at ECTRIMS 2019, the 35th Annual Congress of the European Committee for Treatment and Research in Multiple Sclerosis, taking place in Stockholm, Sweden.

A poster featuring a post-hoc exploratory analysis of measures of thalamic volume from RADIANCE was presented September 11, 2019, at ECTRIMS 2019, the 35th Annual Congress of the European Committee for Treatment and Research in Multiple Sclerosis, taking place in Stockholm, Sweden.
Addressing comorbidities plays an important role in the management of patients with multiple sclerosis (MS), particularly given their association with hospital admissions. In a study using data from the National Patient Sample, comorbidities were linked with patients’ age, sex, and race and ethnicity, said Deborah Taira, MPA, ScD, professor, Daniel K. Inouye College of Pharmacy, University of Hawai‘i at Hilo.
Some data suggest that pregnancy may be beneficial in the long-term for patients with multiple sclerosis (MS), but there exist periods that may carry an extra risk of relapse, such as before conception and in the postpartum period, according to Marie D’hooghe, MD, PhD, neurologist at the National MS Center, Melsbroek, in Brussels, Belgium, and consultant neurologist at the University Hospital in Brussels, Belgium.

Paul Wicks, PhD, vice president of innovation at PatientsLikeMe, discussed the benefits of using technology in multiple sclerosis research by patients, providers, researchers, and other decision-makers.

Despite the benefit of having more choices than ever before to treat patients with multiple sclerosis, the abundance of options has led to more complexity, according to speakers at the 2014 ACTRIMS-ECTRIMS Joint Meeting in Boston, Massachusetts.

259 Prospect Plains Rd, Bldg H
Cranbury, NJ 08512
© 2025 MJH Life Sciences®
All rights reserved.
