Ovarian Cancer
Latest News

Latest Videos

More News
Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists significantly enhance overall survival in patients with ovarian cancer, offering a promising adjunct to traditional treatments.
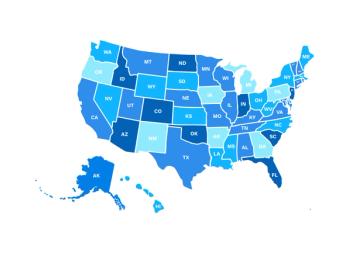
US ovarian cancer mortality rates declined from 1999 to 2020, but significant disparities remain across age, race, and geographic regions, highlighting the need for targeted public health efforts.
An expert discusses how multidisciplinary collaboration can be enhanced through shared knowledge of available drugs and biomarkers among oncologists and pathologists, standardized interpretation methods across different cancer types, and clear communication about trial-specific algorithms to optimize treatment plans and ensure proper biomarker assessment.
Mirvetuximab soravtansine continues to show efficacy and safety in the final analysis of the phase 2 PICCOLO study.
Rucaparib maintenance improved progression-free survival (PFS) in homologous recombination deficiency (HRD)-negative advanced ovarian cancer, irrespective of baseline prognostic factors.

Abstracts published ahead of the 2025 American Society of Clinical Oncology Annual Meeting found persistent ovarian cancer survival disparities among racial and ethnic subgroups, particularly within disaggregated Asian American, Native Hawaiian, and Pacific Islander populations.
Innovative antibody drug conjugates are advancing in ovarian cancer treatment, exploring new maintenance therapies and biomarker-driven approaches for improved outcomes.


CK Wang, MD, chief medical officer of COTA, highlights how a lack of screening tools and declining ob-gyn pipeline can compound historical disparities seen in Black women's access to care.

Facility-level disparities in adopting minimally invasive interval debulking surgery for ovarian cancer highlight urgent needs for equitable care access.
In line with previous clinical trial findings, real-world data show that bevacizumab improves outcomes in patients with epithelial ovarian cancer and high-risk prognostic factors.

A panelist discusses how novel targeted therapies such as antibody-drug conjugates are rapidly evolving in gynecologic oncology, with multiple agents targeting different biomarkers in development, though optimal sequencing strategies remain to be determined.

A panelist discusses how antibody-drug conjugates like mirvetuximab should be sequenced in platinum-resistant ovarian cancer, recommending it as first-line therapy for folate receptor alpha–high tumors due to higher response rates when used earlier.
A panelist discusses how guidelines from organizations like the National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) can improve clinician awareness and adoption of molecular testing in community oncology settings while acknowledging that some effective treatments work across patient populations without requiring biomarker stratification.

A panelist discusses how tumor heterogeneity (both spatial and temporal) affects molecular testing reliability in ovarian cancer, highlighting that although most biomarkers show little heterogeneity, newer approaches like liquid biopsies can provide a more comprehensive genetic profile of the entire tumor burden.

As National Women’s Health Week approaches, new global data highlighting projected rises in breast and ovarian cancer through 2050 is prompting renewed calls for gender-specific prevention strategies that address evolving health risks for women.

FDA approves the first treatment for KRAS-mutated recurrent low-grade serous ovarian cancer (LGSOC), offering new hope for patients with this condition.

A panelist discusses how education and cost are key challenges in ensuring comprehensive molecular testing is performed in a timely manner for patients with ovarian cancer, emphasizing the need for better education of health care providers and more affordable, widely available testing options.

A panelist discusses how multiple molecular biomarkers beyond BRCA and homologous recombination deficiency (HRD) testing are emerging as important for guiding ovarian cancer therapy, including microsatellite instability (MSI), tumor mutational burden (TMB), HER2, p53, KRAS, and CCNE amplification.

A panelist discusses how folate receptor alpha (FRα) expression testing plays a crucial role in determining eligibility for mirvetuximab soravtansine (an antibody-drug conjugate therapy), emphasizing the importance of comprehensive biomarker testing at diagnosis rather than piecemeal testing.

A panelist discusses how National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) guidelines have influenced molecular testing in ovarian cancer, highlighting the importance of biomarkers like BRCA genes for treatment decisions, prognostic information, and family prevention strategies.

New research explores the complex relationship between female infertility and gynecological cancers, revealing minimal links and emphasizing the need for further studies.

Individuals who transition from overweight to obese during adulthood may face a higher ovarian cancer risk, highlighting the importance of tracking body fat changes.

Black and American Indian women with ovarian cancer were less likely to have elevated cancer antigen 125 (CA-125) levels at diagnosis, resulting in delayed chemotherapy initiation and highlighting the need for more inclusive guidelines.

The electronic health record (EHR)–based symptom inventory identified symptom prevalence and associated comorbidities, but no ovarian cancers were diagnosed during the study period.