
The Center on Health Equity and Access provides information on the latest news, research discoveries, and initiatives dedicated to addressing healthcare disparities and improving overall access to high-quality care.

The Center on Health Equity and Access provides information on the latest news, research discoveries, and initiatives dedicated to addressing healthcare disparities and improving overall access to high-quality care.

Authors highlight key aspects of the California Cancer Care Equity Act, including its focus on Medi-Cal beneficiaries, the requirement for managed care plans to contract with specialized cancer centers, and the definition of complex cancers.

Spanning 22 studies, the analysis illuminated housing disparities, occupational hazards, unequal health care access, economic inequality, and discriminatory industry practices and how they collectively contribute to heightened lung cancer risks.
The Obesity Action Coalition and other organizations are urging the FDA to address critical gaps in drug testing, emphasizing the need for specific testing in individuals with obesity to ensure safety and efficacy, as current practices expose this population to unnecessary risks.

The initiative emphasizes equal partnerships between research institutions and community organizations.

The Center on Health Equity and Access highlights the most recent updates in the realm of health equity, including news, research findings, and initiatives focused on mitigating health care disparities and enhancing overall access to quality care.

Alvaro Pascual-Leone, MD, PhD, addresses the role of the gene variant APOE4 in Alzheimer disease and dementia, noting its influence on risk factors and the significance of early diagnosis for effective intervention across all racial groups.

Findings show breathing sounds recorded by smartphones during sleep at home can reliably identify obstructive sleep apnea, presenting an innovative and accessible alternative to traditional in-laboratory polysomnography.

Jeffrey Sippel, MD, MPH, addresses the increasing denial of insurance claims for non-invasive ventilators (NIV) in Medicare Advantage plans, particularly impacting ALS patients, emphasizing the time crunch on patients, and criticizing the financial focus over patients' well-being.
In a trial assessing subcutaneous OCTA101 in patients with severe hemophilia A, promising results in pharmacokinetics and efficacy were overshadowed by safety concerns.

Jeffrey Sippel, MD, MPH, discusses the trend of insurance claim denials related to non-invasive ventilators for patients with ALS.

The Center on Health Equity and Access spotlights the latest health equity news, research, and initiatives to reduce health care disparities and improve access to care.

Postmenopausal women experienced more severe effects, with a 20.1% increase in insulin resistance, according to the findings.

Due to the frequent rejection of claims for noninvasive ventilators by Medicare Advantage plans, individuals with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) are experiencing disproportionately high rates of hospital admissions.
New research highlights racial disparities in hemophilia care, revealing that Black and Hispanic patients are significantly less likely to receive immune tolerance induction treatment compared with White patients, even after considering clinical factors.

“The silencing of Black cancer patient voices impacted patients�’ health care utilization and had implications for their physical health,” the authors wrote.

Industry stakeholders and patient advocacy groups are raising concerns with CMS due to high denial rates for non-invasive ventilators (NIVs) by Medicare Advantage plans.
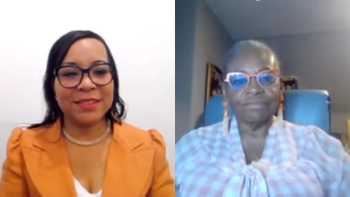
Care in the fourth-trimester, when the birth has taken place and the mother and baby return home, is crucial for the well-being of the mother or the birthing person, Takiyah Durham, MBA, explains in an interview.

Phathom Pharmaceuticals' vonoprazan (Voquenza) sets a new standard in erosive gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) therapy.

Poor sleep and insomnia symptoms were both associated with an increased likelihood of elevated emotional exhaustion among emergency health care workers.

“Our findings further reinforce that place is important and that the social, economic, and health care equity context is key to minimizing health care expenditure disparities for Black adults in the US," investigators explain.

The findings from a recent study unveiled notable distinctions in bleeding rates between etranacogene dezaparvovec and the standard prophylactic factor IX (FIX) products among individuals diagnosed with hemophilia B.

The study identified practical instruments for monitoring physical function in people with hemophilia by pinpointing 11 potential markers and establishing performance-based tests for 5 of these activities.
While clinical trials offer controlled data, real-world studies like HEM-POWR bridge gaps, confirming damoctocog alfa pegol’s effectiveness and tolerance, establishing it as a valuable hemophilia A treatment option.

A pair of studies found the common morning ritual of hitting the snooze button doesn't dilute the quality of sleep and can improve cognitive function after awakening.

Margaret Larkins-Pettigrew, MD, and First Steps and Beyond director Takiyah Durham, MBA, explain how the community-centered program ensures pregnant patients are equipped with resources while receiving equitable care.

Individuals with genetic syndromes or neurodevelopmental conditions experienced shorter and poorer quality sleep, while those with heterogeneous intellectual disabilities had comparable duration but lower quality to controls.

“There are things more important than our discomfort, and there are things that are more important than even our fear—inclusion is more important,” said Erica Marsh, MD, MSCI. “Our care of our patients and loved ones is more important, and our existence tomorrow has to be more important than our fears today.”

Valerie Montgomery Rice, MD, FACOG, a distinguished infertility specialist, highlights the pivotal role of cultural humility, diversity, acknowledgment of historical injustices, and collective action in addressing disparities and fostering equitable access to health care.

In the aftermath of the Dobbs v Jackson Women’s Health Organization ruling, Anita Allen, PhD, highlights the challenges to abortion rights in the United States, emphasizing disparities faced by marginalized communities, outlining threats to reproductive health care, and calling for collective action and advocacy to defend constitutional privacy and uphold the dignity of all individuals.

259 Prospect Plains Rd, Bldg H
Cranbury, NJ 08512
© 2025 MJH Life Sciences®
All rights reserved.
