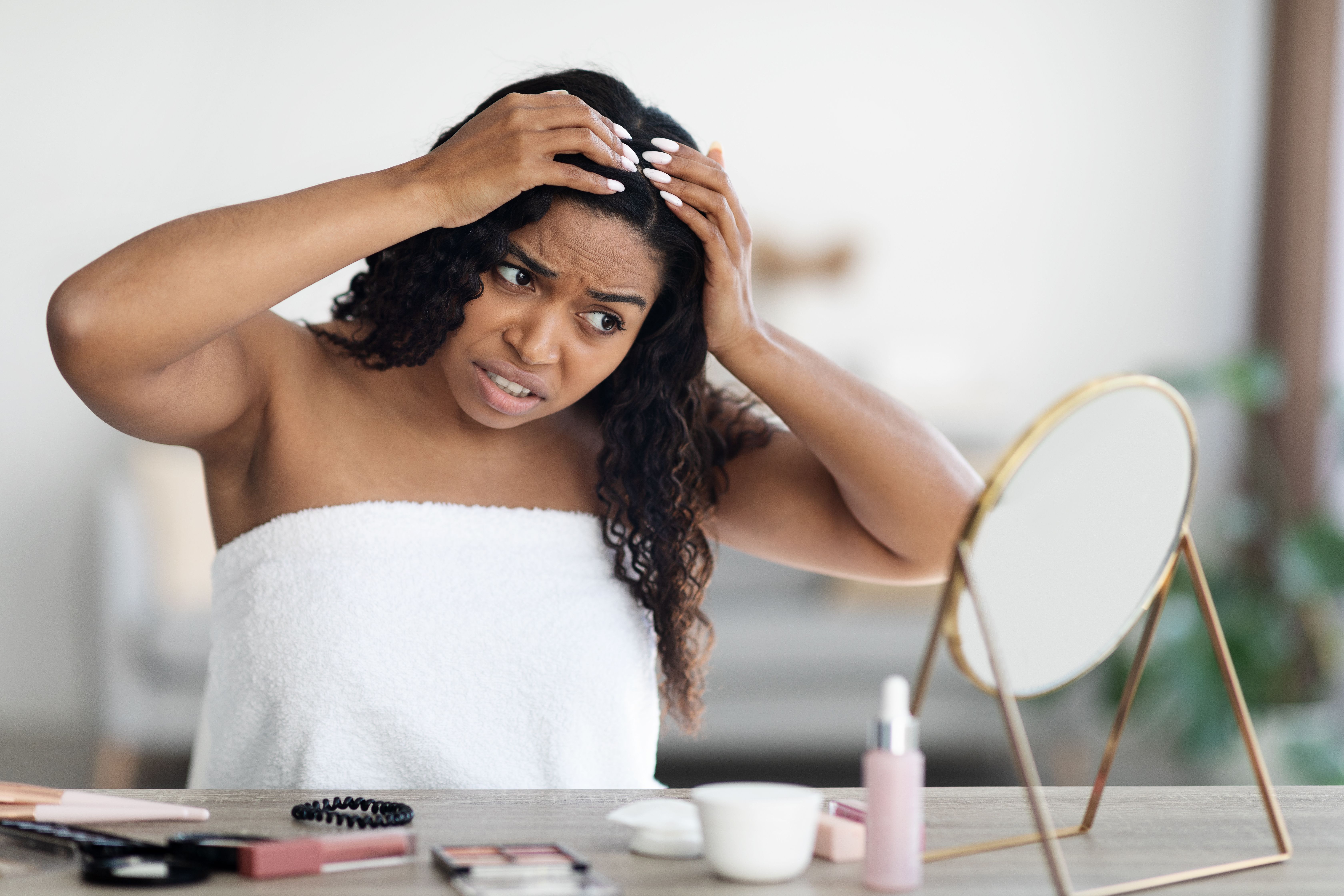
Kristen Whitney, DO, FAAD, dermatologist at Allegheny Health Network, explored the intricate management of alopecia areata, often in tandem with other autoimmune conditions while emphasizing the significance of innovative medications and diagnostic tools, such as dermoscopy, in enhancing patient outcomes.