Researchers aimed to compare the clinical effectiveness of oral anti-osteoporosis drugs based on the observed risk of fracture while receiving treatment through primary care in the United Kingdom and Spain.


Researchers aimed to compare the clinical effectiveness of oral anti-osteoporosis drugs based on the observed risk of fracture while receiving treatment through primary care in the United Kingdom and Spain.
Postoperative and preoperative start of low molecular weight heparin (LMWH) does not change the outcome of mortality or risk of reoperation in patients with hip fractures treated with osteosynthesis, according to a recent study.

A retrospective cohort study by compared different osteoporosis preventative-medications and found that selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERM) had better hip and major fracture risk reductions than alendronate, while strontium ranelate (SR) had poorer hip and major fracture risk reduction than alendronate.
A large meta-analysis did not find any beneficial effects to vitamin D supplementation for reducing fractures, falls, and bone mineral density, according to a recent study published in The Lancet Diabetes and Endocrinology.

Giving zoledronate every 18 months for 6 years reduced the risk of fragility fractures—both vertebral and nonvertebral—in older women with hip bone mineral density indicating osteopenia, a recent study published in The New England Journal of Medicine reported.

The decline in fractures caused by osteoporosis has stagnated, leading bone experts to suspect a lack in osteoporosis diagnosis and treatment guideline adherence. To combat this, the American Society for Bone and Mineral Research (ASBMR) has added 5 clinical care recommendations to prevent secondary fractures in at-risk patients.

Two studies presented at the American Society for Bone and Mineral Research 2018 Annual Meeting last month specifically addressed men’s bone health and compared their risks with those of women.
A recent study compared the fracture risk between osteoporosis and osteopenia.

A recent study found that statin use reduced the risks of osteoporosis, hip fracture, and vertebral fracture in stroke patients by 30% to 40%, and a dose-effect relationship was observed between statin cumulative defined daily doses and decreased risks of osteoporosis and fractures.

Hip fractures (HF) are one of the most common injuries seen in emergency departments among the elderly, but quality care measures for hip fractures are lacking. To that end, a recent report sought to identify optimal quality indicators (QI) for clinical use, but researchers found gaps that need to be addressed.

A study says it found a link between bone mineral density and sleep onset latency in an elderly population.

A 12-month, late-stage study of romosozumab in men aged 55 to 90 years with osteoporosis found that it increased spine and hip bone mineral density (BMD) and was well tolerated.
A study investigating the genetic determinants of fracture risk identified 15 genetic determinants of fracture, which also influenced bone mineral density. Among the clinical risk factors considered, only bone mineral density demonstrated a major causal effect on fracture, while genetic predisposition to lower levels of vitamin D and estimated calcium intake from dairy were not associated with fracture risk, according to the results.

A recent study using data from the Women’s Health Initiative dataset discovered that a higher fracture risk was associated with higher mortality in multiple myeloma (MM) in postmenopausal women.

Twice-yearly treatment with denosumab, a fully human monoclonal antibody, may be associated with increased bone mineral density (BMD) among patients who receive adjuvant aromatase inhibitors (AIs) therapy, according to a recent study.
Fragility fractures are a serious complication of type 1 and type 2 diabetes, but many clinicians who treat patients with diabetes are not aware of the increased risk of these fractures.



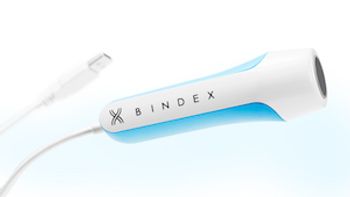
CMS recently approved Medicare coverage for a portable, pocket-sized diagnostic device for osteoporosis when used in ambulatory surgical centers (ASC) and outpatient hospital settings.
The diagnosis of osteoporosis is typically determined by bone mass density (BMD); however, bone turnover markers (BTMs) can provide information involving the bone remodeling process. A recent study found that BMD correlates negatively with BTM and positively with estradiol (E2) and magnesium (Mg(2+)) levels, and tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase-5b (TRAP-5b) demonstrates a specificity in identifying patients with postmenopausal osteoporosis.



Persistent use of osteoporosis medications was associated with reduced risk of fracture and significantly lower total healthcare costs, a recent analysis of Medicare claims data found.

259 Prospect Plains Rd, Bldg H
Cranbury, NJ 08512
© 2025 MJH Life Sciences®
All rights reserved.
