Breast Cancer
Latest News
Latest Videos

CME Content
More News

Less than 1% of all breast cancers occur in men, making this a rare disease among that patient population, and most treatment guidelines are based on outcomes and survival rates seen in women with the disease.
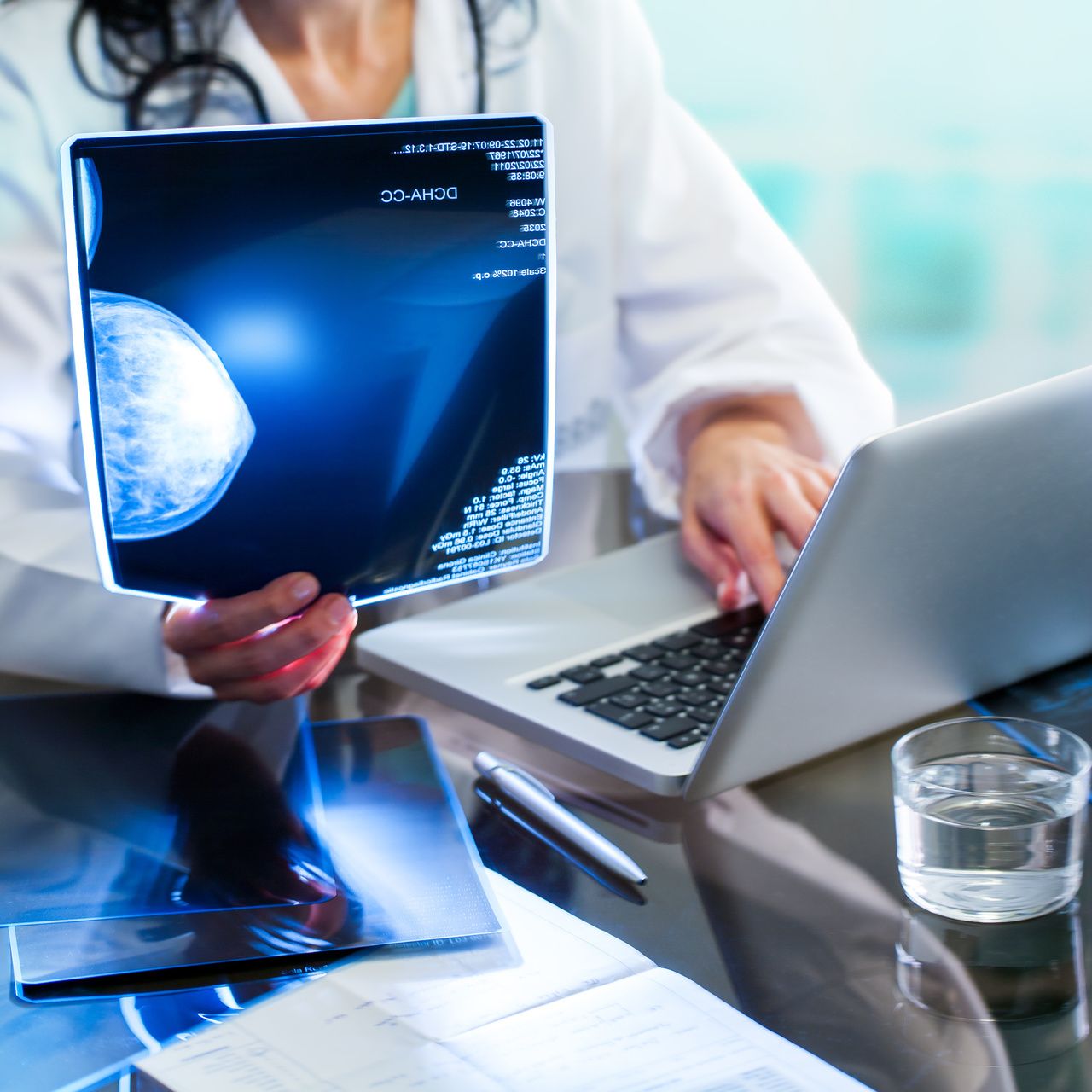
Compared with digital mammography, digital breast tomosynthesis, also called 3-dimensional (3-D) mammography, has been proven superior at effectively detecting breast cancer and leading to fewer recall visits, but more information is needed for how subgroups of women with different breast densities benefit from the screening method, especially those classified as having extremely dense breast tissue.

Women with early-onset germline BRCA-mutated breast cancer can have subsequent pregnancies without increasing their risk for disease recurrence, according to the authors of a recent study in Journal of Clinical Oncology.
The next several years could bear witness to thousands of additional deaths from cancer that could have been prevented through routine diagnostic care that was delayed because of the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic, according to a pair of studies in The Lancet Oncology.
Because male breast cancer is such a rare disease, few strides have been made that convey advantages in its detection, incidence, and mortality. Most treatment guidelines have been extracted from studies performed among female patients.
Breast cancer diagnosed in the year following a negative result after a mammogram has now been associated with an increase in mortality compared with breast cancer detected at a screening, report JAMA Network Open study results.

Smoking history can both increase the risk of cancer and create a hypoxic environment within the body, leading to poor outcomes, including less-effective treatment, among patients who undergo radiotherapy.

In survivors of childhood cancer, early initiation of annual breast cancer screening with MRI, with or without mammography, may reduce breast cancer mortality by half or more, according to a study published in Annals of Internal Medicine.

Despite ongoing disparities in the use of health care services among races/ethnicities and ages, as well as by insurance status, African American women with advanced breast cancer benefited the most following implementation of the Affordable Care Act in states that chose to expand Medicaid coverage.