
Diabetes
Latest News

Latest Videos

Podcasts
CME Content
More News

New findings add to the relationship between red meat and processed meat consumption and the risk of type 2 diabetes.

The expanded approval for the Omnipod 5 system now allows automated insulin delivery (AID) for adults with type 2 diabetes, offering a new option for better glucose management without daily injections.

New findings add to the pile of research on the possible neuroprotective effects of drugs like dapagliflozin, empagliflozin, and dulaglutide for patients with type 2 diabetes.

Diabetic macular edema treatment options include anti-vascular endothelial growth factor (anti-VEGF) injections and laser therapy, with patient-specific factors guiding the best approach.

Despite guidelines recommending annual screenings, nearly half of patients with diabetes miss critical eye exams, explains Jose A. Martinez, MD, president and retina specialist at Austin Retina Associates.

This article describes the trajectory of adherence patterns among users of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors. The authors found that baseline factors were unable to predict the adherence trajectory groups.

Smokers with diabetes on Ozempic are less likely to receive smoking cessation interventions; initiative incentivizes hospitals to eliminate medical debt for low- and middle-income patients; high costs prevent mental health treatment.

Older adults with the most irregular sleep durations demonstrated a 34% higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes compared with those with the most regular sleep.

Up to one-third of Americans have been affected by data stolen through the Change Healthcare cyberattack; research highlights potential cognitive and psychiatric benefits of semaglutide; over 40 Iowa hospitals have ended their labor and delivery services.

On this episode of Managed Care Cast, we're talking with the chief medical officer of CVS Health about recent pharmaceutical innovations, patient-provider relationships, and strategies to reduce drug costs.

CMS recently launched a voluntary, nationwide dementia care program; the number of physicians who reported at least 1 symptom of burnout has dropped below 50% for the first time since the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic; diabetes drugs have all been in short supply over the last 18 months, partly due to people using them off label for weight loss.

Among patients with type 2 diabetes, glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists reduced their risk of obesity-related cancers more than insulin did.

The University Hospitals CINEMA program aims to address issues and narrow gaps in obesity management, with a focus on meeting patients where they are and providing them tools for success, says Ian Neeland, MD.

Robert Lustig, MD, MSL, explains how the US health care industry needs to shift from measuring body mass index and obesity to measuring cardiometabolic health, which affects 93% of Americans, including children.

Change Healthcare will begin notifying individuals whose data may have been exposed when hackers disrupted the claims processing system; experts advocate for early diagnosis of gestational diabetes to mitigate risks for both mother and child; researchers worry that the slow rollout of bird flu tests may hinder outbreak detection and response.
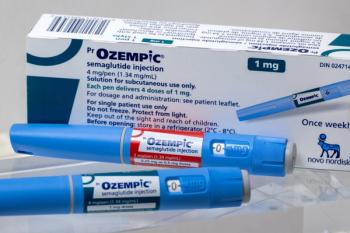
Taking falsified semaglutide (Ozempic; Novo Nordisk) can lead to ineffective treatment due to incorrect dosing, contamination, and the use of unknown ingredients, the World Health Organization (WHO) is warning.

Patients with diabetes who have private insurance are more likely to be prescribed a continuous glucose monitor (CGM) compared with those with government insurance, says Chase Hendrickson, MD, MPH, Vanderbilt University Medical Center.

Children aged 10 years and older with type 2 diabetes can now improve their glycemic control with a drug previously only approved for adults.
Patients who took the weekly glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist were 21% less likely to experience major kidney disease events and 29% less likely to die due to cardiovascular causes.
Other findings from the latest Kaiser Family Foundation Health Tracking Poll shed light on public awareness, use, and opinions on Medicare coverage of glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) drugs.

Survey results from more than 1500 patients with diabetes revealed that 57% believed glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) weight loss drugs alone could be a "silver bullet" for managing their health goals.

Joanne Mizell shares insurer strategies in addressing the escalating rates of metabolic diseases, highlighting the importance of holistic treatment methods like lifestyle modification programs, which integrate nutrition, physical activity, and community engagement.

Yael Mauer, MD, MPH, discusses the patient population who benefits most from interventions with glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) therapies and explores the underlying mechanisms at work.

Stacey Ehrenberg, MD, discusses the lacking data and potential implications of using glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists during pregnancy for patients with diabetes and/or obesity.

Diana Isaacs, PharmD, chair of a recent Institute for Value-Based Medicine® event hosted in conjunction with Cleveland Clinic, details the up-and-coming therapies impacting the scope of treatment in diabetes, obesity, and cardiometabolic health, as well as their associated challenges.














