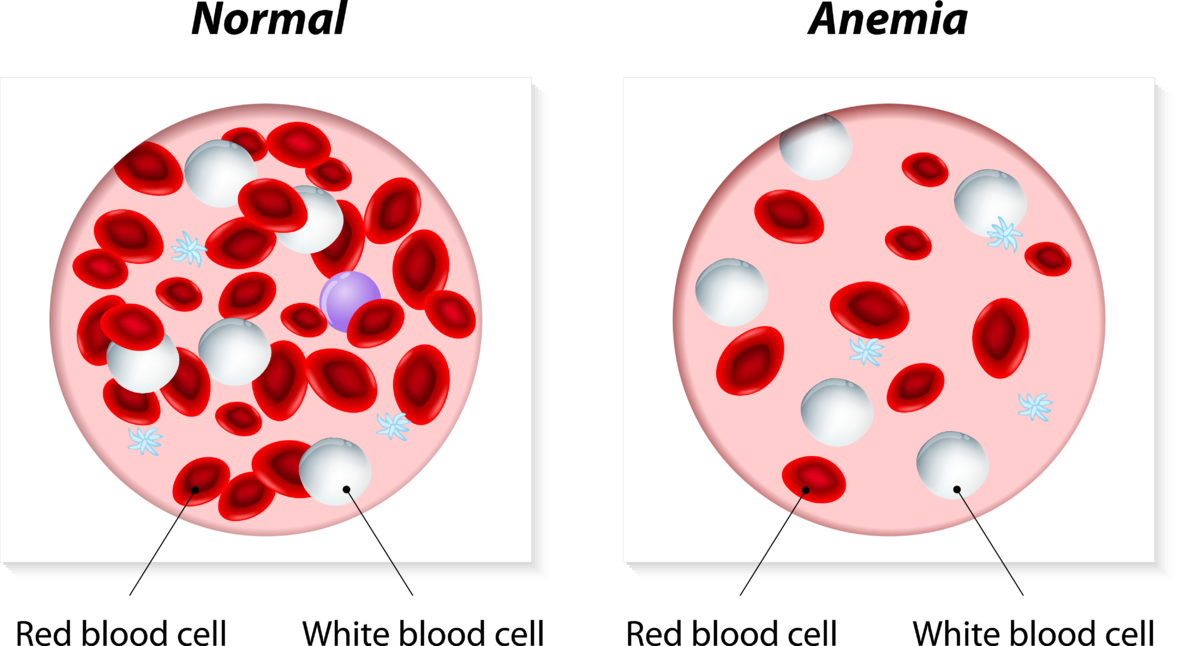
Yale's Silvio Inzucchi, MD, who has been involved in groundbreaking trials with SGLT2 inhibitors for the past decade, shared data that show patients who did not have type 2 diabetes (T2D) when they started the DAPA-HF trial were 32% less likely to develop the disease if they took dapagliflozin (Farxiga) instead of placebo.