Breast Cancer
Latest News

Latest Videos

CME Content
More News

Mei Wei, MD, an oncologist specializing in breast cancer at Huntsman Cancer Institute at the University of Utah, discusses advancements in breast cancer treatment, highlighting CDK4/6 inhibitors and antibody-drug conjugates as promising alternatives to traditional therapies.

Patients with endocrine-resistant, HER2-negative, locally advanced or metastatic breast cancer can use the treatment after recurrence or completing adjuvant endocrine therapy.
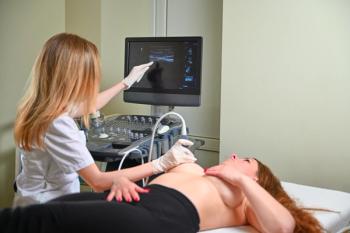
Here are 5 key points for pre–breast screening preparation that cover the areas of risk assessment, lifestyle adjustments, understanding screening details, managing anxiety, and open provider communication.

In this interview from our Institute for Value-Based Medicine® event in Boston, we speak with Michael Hassett, MD, MPH, Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, on the clinical significance and cost implications of HER2 in the breast cancer space.
Hereditary breast cancers are caused by germline mutations, which are genetic mutations inherited at conception and so called because they originate in germ cells, those that develop into reproductive cells and become eggs in female individuals and sperm in male individuals.

The American Cancer Society (ACS) 2024 report emphasizes significant racial disparities in breast cancer outcomes and calls for increased efforts to improve equity in screening and treatment.
World Dense Breast Day emphasizes the need for awareness and advocacy for individuals with dense breasts, which can negatively impact mammogram results and increase breast cancer risk.

The FDA approved ribociclib (Kisqali) for adjuvant treatment of high-risk, hormone receptor-positive, HER2-negative early breast cancer.

Disparities continue in younger patients, raising the need for novel interventions to mitigate challenges associated with younger age at diagnosis.

Mammography facilities are now nationally required to inform patients about their breast density, which can affect cancer detection.

Using artificial intelligence (AI) in breast cancer screenings in the United Kingdom could be cost-effective and improve health outcomes after identifying more cancers.

While it can seem overwhelming or difficult to decide where to start addressing racial and ethnic disparities in health care, the key is to focus on a manageable area that can be built upon.

A new review highlights the urgent need for research-driven solutions in breast cancer to enhance early detection, treatment, and patient support across diverse populations.

Demetria Smith-Graziani, MD, MPH, Emory University School of Medicine, explained biological and structural obstacles to equitable breast cancer outcomes and care across racial and ethnic groups.

Artificial intelligence (AI) can aid in breast cancer detection, but radiologists need training to ensure accuracy and prevent missed cancers.

A panel of experts review ASCO 2024 and the need for future research in CDK4/6 inhibitors.

Harold "Hal" Burstein, MD, PhD, emphasizes the crucial role of strong patient-physician partnerships in breast cancer treatment, empowering patients through shared decision-making.

The COVID-19 pandemic disrupted breast cancer screenings, leading to decreased follow-up rates and widening health disparities.

Dr. Dempsey discusses how CDK4/6 Inhibitors have impacted medication costs for breast cancer care, and the importance of implementing cost containment strategies to alleviate the situation.

Drs. Hanna and Rugo discuss possible access improvements in regards to CDK4/6 inhibitors.

The risk of early-onset breast cancer, particularly luminal A and triple-negative subtypes, was higher in Black women with obesity and high leptin levels compared with White women. This research highlights the urgent need for targeted interventions to address racial disparities in breast cancer outcomes.

Dr. O’Shaughnessy discusses how she weighs clinical benefits against cost considerations in regards to selecting a CDK4/6 inhibitor.

A panel of experts discuss the variables of dosage and patient adherence in regards to managing toxicities from CDK4/6 inhibitors.

A medical expert navigates toxicity management in patients being treated with ribociclib.

Dr. Rugo details her management strategy in regards to GI toxicities.