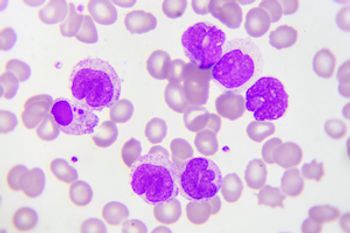
Patients with myelofibrosis who were treated with Janus-kinase (JAK) 1/2 inhibitors have an increased risk for developing B-cell lymphoma. However, researchers believe there is a pre-existing B-cell clone that patients can be tested for before treatment.