
Multiple Myeloma
Latest News

Latest Videos

More News

The FDA granted accelerated approval to talquetamab on August 9, 2023, as a treatment option for adult patients with relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma (RRMM) who have failed at least 4 prior lines of therapy.

Treatment and management of multiple myeloma (MM) is continuously evolving, and in this analysis, investigators discuss ever-present issues and potential solutions to optimize care for this patient population.

Most recently, the FDA’s Oncologic Drugs Advisory Committee unanimously voted to recommend ciltacabtagene autoleucel (Carvykti; Johnson & Johnson) in patients who have received at least 1 line of treatment for relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma (RRMM).

Idecabtagene vicleucel (ide-cel) was able to triple progression-free survival and reduce the risk of disease progression or death in a phase 3 trial.

Investigators used the Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy-General General Physical Wellbeing Scale to collect data on patient-reported treatment-related adverse effects, to provide clinicians guidance on predicting risk of early treatment discontinuation among ECOG-ACRIN E1A11 trial participants.
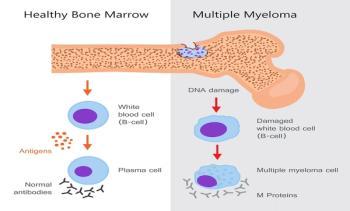
In this analysis, 3 bisphosphonates (alendronate, pamidronate, and zoledronic acid) and 1 RANK ligand inhibitor (denosumab) were evaluated for their effectiveness at preventing osteoclasts from facilitating jaw degradation and reducing vertebral fracture risk among patients being treated for multiple myeloma.

Teclistamab (Tecvayli, Johnson & Johnson), a first-in-class bispecific T-cell–engaging antibody, is approved to treat relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma in the US.

The FDA recently approved the supplemental biologics license application for teclistamab (Tecvayli; Johnson & Johnson) to treat relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma on a biweekly dosing schedule.

Teclistamab (Tecvayli) was first approved for use in patients who have relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma (RRMM) in October 2022, making it a first-in-class bispecific antibody.

An on-body delivery system approved last fall for paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH) has seen rapid uptake and is now being studied for use with isatuximab.

The bispecific antibody is used to treat patients with relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma (R/R MM) who have achieved and maintained a complete response for at least 6 months; this approval allows a dosing frequency of 1.5 mg/kg every 2 weeks.

The combination of daratumumab and immumodulatory therapy was evaluated among patients with relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma (RRMM) who have failed prior treatment with immunomodulatory agents, proteasome inhibitors, and daratumumab as monotherapy or in combination.

Clinical investigators evaluated the impact of home health services on disability status and receipt of treatment among adults 66 years and older with a new diagnosis of multiple myeloma (MM).

Patient survival and such treatment-related outcomes as time to treatment failure and treatment duration improved following implementation of a best practices program that focused on selinexor administration for multiple myeloma (MM), with implications for other anticancer medications.

A claims-based study analyzing Medicare beneficiaries with multiple myeloma found that racial disparities still impact treatment in this patient population.


This literature review investigated outcomes related to relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma (MM) among patients 65 years and older.
Patients with multiple myeloma are living longer; therefore, their lifelong treatment expenses can become burdensome.

A qualitative interview study gauged patients’ experiences with belantamab mafodotin, which is used to treat relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma (RRMM) following failure on at least 4 prior therapies.

Real-world patients were on average older and had more comorbidities than those in clinical trials, factors previously seen in comparisons between patients in clinical trials and real-world settings.

The most-read articles from the 2023 European Hematology Association (EHA) Annual Meeting covered the most up-to-date treatment strategies for hematological malignancies, racial disparities in treatment patterns for blood cancers, and updates on immunotherapy as a tool in hematologic oncology.

Regeneron officials say they are on track to file for FDA approval for the bispecific antibody by the end of 2023.
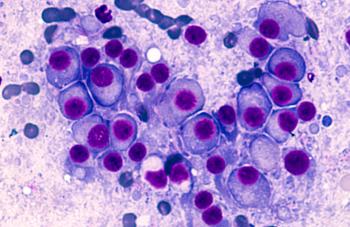
Real-world data presented at the 2023 American Society of Hematology Annual Meeting and Exposition showed similar toxicity profiles and outcomes among older and younger patients with multiple myeloma (MM) treated with teclistamab.


Our top multiple myeloma (MM) content this year included research suggesting many patients still face poor prognoses despite advances, a case study of unique MM presentation, and research presented at the 2022 American Society of Hematology Annual Meeting.












