Respiratory
Latest News
Latest Videos

Shorts

Podcasts
CME Content
More News

Telemedicine improved the quality of life and inhaler technique among patients with advanced-stage chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).

Paternal prepubertal passive smoke exposure is linked to impaired lung function trajectories in offspring, persisting into adulthood.

Syndromic reverse transcriptase–polymerase chain reaction tests for respiratory infections were associated with lower health care resource utilization and costs, implicating potential for improved value in patient care.
Mepolizumab showed significant real-world improvements in asthma outcomes, reducing exacerbations and corticosteroid use in severe eosinophilic asthma.

Patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) who smoke were less likely to receive tobacco dependence treatment (TDT) if they lived in rural areas or had longer travel times to care, highlighting persistent geographic disparities in access.

The FDA approved zopapogene imadenovec, the first therapy for recurrent respiratory papillomatosis, providing an option beyond repeated surgeries to manage the rare condition.
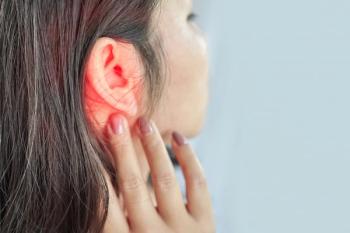
Biologic therapies for severe asthma and chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps (CRSwNP) significantly improved ear-related symptoms, enhancing patient quality of life and treatment outcomes.

Multidisciplinary Approaches to Pediatric Obstructive Sleep Apnea: A Review of Respiratory Therapies
The treatment of pediatric obstructive sleep apnea syndrome is moving toward a personalized, multidisciplinary approach that combines surgical options with a growing number of nonsurgical alternatives, to better address the unique needs of each child.

Machine learning holds promise for optimizing treatment strategies and potentially improving outcomes in respiratory failure but future research and development are necessary to fully realize its potential in clinical practice.

Despite their devastating global impact, chronic respiratory diseases remain a hidden threat in low- and middle-income countries, often going undiagnosed in adults who are already battling other noncommunicable diseases.

Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) poses a significant, often overlooked, risk for serious cardiovascular complications in older adults, underscoring the need for vaccination in this population regardless of their preexisting health conditions.
Air pollution exposure, both before and after birth, significantly escalates the risk of respiratory infections in children.
Depemokimab significantly reduces asthma exacerbations, benefiting patients regardless of their baseline asthma control levels. A biologics license application for depemokimab is currently being reviewed by the FDA.

A phase 2a trial of camlipixant, a selective P2X3 receptor antagonist, found that while the drug did not significantly reduce cough frequency in the overall population with refractory chronic cough, it produced meaningful improvements in patients with a higher baseline cough burden.

Compared with tezepelumab, solrikitug demonstrated unique epitope binding and superior potency across several assays.

Remote care reduced readmissions and improved functional outcomes in COPD in a recent study.

The CDC’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices was expected to meet later in June to issue recommendations for use.

A new device was able to distinguish between mild and very severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).

Respiratory diseases made up the hospitalizations in older adults after they were exposed to wildfire smoke.

Smoking prevalence is projected to decline by 2035, yet health consequences persist due to slower reductions among older adults.
Patients with progressive pulmonary fibrosis who received nerandomilast showed improved forced vital capacity from baseline at 52 weeks in the phase 3 FIBRONEER-ILD trial.

Both candidates combine 2 already licensed vaccines to prevent influenza and COVID-19.

These data from the Environmental Protection Agency were presented at the Society for Risk Analysis annual meeting.

New York City data highlight the benefits of early administration of nirsevimab to safeguard infants from respiratory syncytial virus (RSV).