
Diabetes
Latest News

Latest Videos

More News

The 6 finalists will pitch their innovations at Google’s campus February 27 for a chance to win up to $50,000 in in-kind services from Boston Scientific and Google.

The use of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors leads to cardiovascular benefits in all patients with type 2 diabetes (T2D), according to a study recently published in the Journal of the American Heart Association.

There’s not much research available comparing the Paleolithic diet to other popular nutritional plans. A new study sought to scour existing data to see the Paleolithic diet’s effect on glucose and insulin regulation. The data showed no significant impact.

The 2007 paper examined the elevated risks for cardiovascular disease and type 2 diabetes for patients who have schizophrenia or bipolar disorder.

Results showed that managing T1D becomes more intense during pregnancy and in the months that follow childbirth. This is due to the need to be even more vigilant than usual in monitoring blood glucose levels and dosing insulin, tasks the women performed mostly themselves, but which can also be performed by other healthcare professionals.

Data collected between 1995 and 2014 show prevalence and incidence of diabetes are substantially higher in First Nations people in Canada compared to other people in Ontario, according to a study published in the Canadian Medical Association Journal.

Atul Grover, MD, PhD, the executive vice president for the Association of American Medical Colleges, sat down with Representative Lauren Underwood, D-Illinois, for a conversation about her healthcare-related efforts during her first year in Congress representing people from a suburban rural district 2 hours from Chicago.

Researchers discovered a link between circadian clock disturbances in pancreatic cells and type 2 diabetes (T2D), according a study published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
For the first time, scientists obtained high-definition images of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptors, enabling future research into treatments for type 2 diabetes, according to a study published in Nature Communications.

Jeffrey D. Dunn, PharmD, MBA, has served as vice president of clinical strategy and programs and industry relations at MagellanRx, a national pharmacy benefit manager (PBM); cofounder, senior vice president, chief clinical officer, and board member of VRx, a regional PBM; and pharmacy director of SelectHealth, part of Intermountain Healthcare. Dunn was instrumental in opening and running the VRx retail pharmacy in downtown Salt Lake City, Utah. He is a board member of Care Pharmacies Cooperative, a chain of 100 retail pharmacies. An editor from The American Journal of Managed Care® recently conducted a question-and-answer session with Dunn regarding the recent Institute for Clinical and Economic Review report on the cost-effectiveness of oral semaglutide.
Results from an analysis conducted by the Pharmacy Benefit Management Institute (PBMI) show that the use of Jardiance (empagliflozin) among employees with type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease can save employers around $737,000 per 10,000 covered lives each year.
Novo Nordisk announced Thursday the FDA has approved injectable semaglutide (Ozempic) for adult patients with type 2 diabetes (T2D) and known heart disease.

The implementation of the Smart Snacks in School standards in 310 public schools resulted in healthier dietary intakes among students compared with those without the standards, according to a JAMA study published January 15.

The FDA expanded the use of Fiasp, a fast-acting insulin aspart injection, in children as young as 2 years to treat diabetes. First approved for adults in 2017, Novo Nordisk said it is the only "mealtime insulin injection that does not have a pre-meal dosing recommendation.”

Heart disease and kidney disease are widely known comorbidities of diabetes, but a lesser-known complication that dramatically effects between 10 million and 20 million American adults is peripheral arterial disease (PAD). In its most extreme form, PAD can lead to limb loss.

The workshops were aimed at ensuring that primary care centers were following clinical care guidelines developed after 2011 meeting requirements of a national certification program.

This week, the top managed care stories included the FDA announcing a ban on flavored e-cigarettes; Google’s artificial intelligence system can find breast cancer as well as experts; new diabetes guidelines including 2 new drug classes to treat comorbidities.
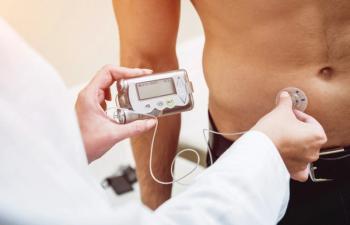

The significant findings of the DAPA-HF data have been well received in both the scientific and payer communities, but we also need to ensure that patients with diabetes are educated on the signs, symptoms, and risk factors linked with heart failure, said Kiersten Combs, BS, US vice president of Cardiovascular Metabolism at AstraZeneca.

Advances in continuous glucose monitoring, reimbursement for genetic testing, and payment models in oncology care were popular with readers of the Evidence-Based series.
Although there were many updates in various facets of diabetes care, one change stood out. New recommendations call for 2 drug classes to be used to treat patients with type 2 diabetes (T2D) and comorbidities: sodium glucose co-transporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors and glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists.

We are in the regulatory process to get an indication for the treatment of heart failure in both type 2 and non-type 2 diabetic patients, and this serves as just the start of the scientific investment that we have made with dapagliflozin, said Kiersten Combs, BS, US vice president of Cardiovascular Metabolism at AstraZeneca.
Researchers constructed a risk prediction model of hospitalizations due to heart failure (HHF) for patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), according to a Clinical Cardiology study.
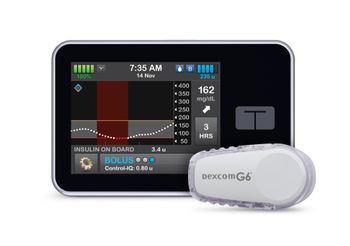
The company said that with the clearance, the FDA outlined standards for a new device category, the interoperable automated glycemic controller designation.

















