Skin Cancer
Latest News
Latest Videos
More News

Many talks at the Association of Cancer Care Centers (ACCC) 41st National Oncology Conference advocated for the adoption of culturally relevant care, the leveraging of community partnerships, and community engagement to build better trust with patients and improve outcomes.

The announcement followed the release of the RhodoLED XL red light-emitting lamp, to be used in combination with aminolevulinic acid hydrochloride topical gel, 10% for actinic keratoses.
Of 7 subtypes identified 10,000 melanoma cells, C4 Melanoma COCO1A was the only to show indications of being more sensitive to natural killer (NK) and T cells.

A poster presented at the 2024 American Society of Clinical Oncology annual meeting argued the benefits that Medicaid expansion can bring to patients with melanoma.

Two posters presented at the 2024 American Society of Clinical Oncology annual meeting revealed real-world data on the outcomes and management strategies associated with melanoma during pregnancy.
At the 2024 American Society of Clinical Oncology annual meeting, an abstract presenting real-world data stressed the need for further research regarding the association between immunosuppressant medication and the development of skin cancer.
Metformin showed promise for improving the overall survival rate of patients with melanoma; however, this result may be an indirect consequence of the drug.
A large Medicare cohort study found that the most common locations of procedurally treated keratinocyte cancers in the US were the head and/or neck for both squamous cell carcinomas and basal cell carcinomas.

An analysis that overviewed dermatologic mobile apps with artificial intelligence (AI) features led researchers to voice concerns about the use of this technology in its current state.
A follow-up study utilizing interviews and survey responses demonstrates that patients prefer rhenium-188 skin cancer therapy (RSCT) over surgery in the treatment of their non-melanoma skin cancer.

A cross-sectional, mixed-methods study found that adverse effects (AEs) can occur even after 1 year of treatment with immune checkpoint modulator (ICM) therapy in patients with melanoma.
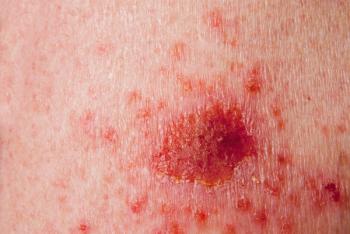
A systematic analysis demonstrated the rarity of super-giant basal cell carcinomas and the need for further characterization of these understudied skin cancers.
The study aimed to improve the understanding of lived experiences and the fear of recurrence among survivors of localized, stage 0 to IIA cutaneous melanoma.
A retrospective analysis out of Denmark could not find a causal relationship to explain trends in melanoma incidence and mortality rates, demonstrating the need for more research in this area.
Michael Farwell, MD, associate professor of radiology at the Hospital of the University of Pennsylvania, provides insights into a study on the benefits of using 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) PET/CT imaging to detect metabolic tumor changes in skin cancer.

A prospective study evaluating the efficacy of an artificial intelligence (AI)–based clinical support system further demonstrated the reliability of AI or machine learning as a diagnostic tool in skin cancer.
A retrospective study analyzing tissue assays from patients with cutaneous melanoma demonstrated the promise of yes-associated protein (YAP) as a predictive biomarker for melanoma prognosis.

An artificial intelligence (AI) mode was more accurate in assessing patient risks for skin cancer through the analysis of 2D facial images compared with more traditional risk-factor screening.
A population-based cohort study out of Norway has found that older men have a higher risk of developing second primary invasive melanoma following an initial primary melanoma, suggesting the benefits of increased surveillance in these patients.
Results from a retrospective cohort study analyzing patients with breast cancer bolster reports of an association between radiation therapy and subsequent risks of skin cancers.

A multicentric, single-arm diagnostic study created a decentralized federated learning model for the classification of invasive melanomas and nevi, showcasing comparable results to centralized data models.
A retrospective, cross-sectional study analyzed national trends of immunohistochemistry (IHC) use in the diagnosis of melanoma.

A comparative analysis on skin cancer management guidelines in the US highlights the necessity of further research in this subject.
An ecological study revealed increasing rates of skin cancer overdiagnosis in white Americans.

Andrew Ress, MD, discusses the novel integration of artificial intelligence (AI) into the skin cancer treatment landscape.