Type 1 Diabetes
Latest News
Latest Videos

CME Content
More News

Tom Robinson, vice president of global access at JDRF, talks about the data collection process in creating the Type 1 Diabetes (T1D) Index.

Considerable research on diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) risk has been published since the publication of a 2011 systematic review, warranting an updated analysis.

Tom Robinson, vice president of global access at JDRF, talks about the predictive modeling exercise used to develop and refine the Type 1 Diabetes (T1D) Index.

Serum α-synuclein was found to be increased in children with obesity and type 1 diabetes (T1D), which was linked to the impairment of executive function in these children.

According to Tom Robinson, vice president of global access at JDRF, the creation of the Type 1 Diabetes (T1D) Index was prompted by a lack of basic data on the condition, such as how many people are living with and affected by T1D.

People with diabetes in Italy and the United Kingdom reported the highest rates of anxiety at 63% and 51%, respectively.

Tom Robinson, vice president of global access at JDRF, explains how to navigate the Type 1 Diabetes (T1D) Index and what data can be pulled from it.
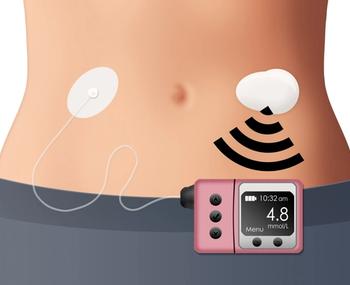
The bionic pancreas uses algorithms to continually adjust insulin doses based on the user’s needs, requiring less user input compared with other existing artificial pancreas technologies.
The Type 1 Diabetes (T1D) Index measures global T1D prevalence and provides other statistics and estimates related to the autoimmune condition.

In 2040, researchers predict between 13.5 and 17.4 million type 1 diabetes (T1D) cases globally, reflecting a 60% to 107% increase in cases compared with 2021.

A deal was reached to renew 5-year FDA user fee programs; children and adolescents with COVID-19 had a 60% increased risk of developing type 1 diabetes (T1D); states cannot penalize Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) employees for facilitating abortions permitted by federal law.

Children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes (T1D) saw improved quality of life (QOL) and metabolic control when using an advanced hybrid closed-loop (AHCL) insulin delivery method vs conventional therapy.

Treating children with mild diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) using subcutaneous (SC) insulin aspart was linked to lower hospital costs and better efficacy of DKA management, compared with using intravenous (IV) insulin.

Women with type 1 diabetes (T1D) had a better cardiometabolic risk factor profile but did not have a significantly lower cardiovascular disease (CVD) event burden compared with their male counterparts.

A narrative review found that some risk factors may be associated with cognitive impairment in patients with type 1 diabetes.

People with type 1 diabetes (T1D) who partake in fasting during Ramadan may benefit from using an advanced hybrid closed loop (AHCL) insulin pump system.

The next step for health care professionals is to teach patients how to act on the data collected by intermittently scanned glucose sensing technologies, according to Viral Shah, MD, an endocrinologist and scientist.

A recent review examined to what extent childhood obesity increases the risk of various autoimmune diseases in adulthood, including type 1 diabetes (T1D), and the benefits that accrue if weight reduction begins in early life.

A study found cystatin C, renal resistance index, and urinary kidney injury molecule-1 were significantly associated with risk of diabetic kidney disease (DKD) in children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes (T1D).

Researchers achieved successful reactivation of pancreatic stem cells to become insulin expressing, suggesting future potential for replacing destroyed beta cells in patients with type 1 diabetes with newborn insulin-generating cells.

More efforts need to be made to remove unconscious bias when implementing approved diabetes technologies into clinical practice for all patients, said Viral Shah, MD, an endocrinologist and scientist.
The National Health Service (NHS) in England has made the Dexcom ONE real-time Continuous Glucose Monitoring System available by prescription to patients with type 1 diabetes (T1D).

Compared with sensor-augmented pump therapy, closed-loop insulin delivery increased glucose time in range and reduced hypoglycemia episodes but detracted from sleep quality.

While therapies for type 1 diabetes (T1D) are becoming more advanced, the problem is patients can't access them, said Viral Shah, MD, an endocrinologist and scientist.

Viral Shah, MD, an endocrinologist and scientist, discusses ongoing research on preventing bone fractures in people with type 1 diabetes (T1D).