The EMPEROR trials could lead to new indications for the SGLT2 inhibitor for patients with and without diabetes.
Mary Caffrey is the Executive Editor for The American Journal of Managed Care® (AJMC®). She joined AJMC® in 2013 and is the primary staff editor for Evidence-Based Oncology, the multistakeholder publication that reaches 22,000+ oncology providers, policy makers and formulary decision makers. She is also part of the team that oversees speaker recruitment and panel preparations for AJMC®'s premier annual oncology meeting, Patient-Centered Oncology Care®. For more than a decade, Mary has covered ASCO, ASH, ACC and other leading scientific meetings for AJMC readers.
Mary has a BA in communications and philosophy from Loyola University New Orleans. You can connect with Mary on LinkedIn.

The EMPEROR trials could lead to new indications for the SGLT2 inhibitor for patients with and without diabetes.

Two studies, including one that examined patient data from a well-known diabetes trial, confirmed the value of 2 cardiovascular biomarkers in predicting mortality in peripheral artery disease.

Authors say more work is needed to understand the mechanisms behind their findings.




When asked why drug prices are so high, manufacturers offer some version of the same answer: the cost of research and development. Although there is debate over how much it actually costs to bring new therapies to market, a 2016 study by Tufts University put the price tag at $2.56 billion (in 2013 dollars), and researchers found costs were rising 8.5% a year. Failure rates of drugs also contribute to their high prices. A 2018 paper coauthored by Andrew Lo, PhD, of the Massachusetts Institute of Technology found that the probability of success in clinical trials was 13.8%, but the success rate within just oncology was 3.4%.

A year ago, the National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) added the word “accessible” to its mission statement, stating that the group is “dedicated to improving and facilitating quality, effective, efficient, and accessible cancer care so that patients can live better lives.”

More and more, stakeholders across the healthcare system— providers, commercial payers, pharmaceutical companies, large employers, state Medicaid officials, and even state budget officers—are grappling with the fact that the old pay-as-you-go way of covering medicines, even cancer drugs, was not built for these revolutionary therapies. A group at MIT is developing new models, which use reinsurance and payments over time to fund these durable treatments.

Merck's Center for Observational and Real-World Evidence has spent several years gathering evidence on clinical inertia and is now working on solutions to overcome it at the point of care.

There was something for everyone at the American Diabetes Association (ADA) Scientific Sessions, held June 7-11, 2019, in San Francisco, California.
Results were presented recently at the 79th Scientific Sessions of the American Diabetes Association.
The consensus report was presented at the 79th Scientific Sessions of the American Diabetes Association in San Francisco, California.
Selected technology news briefs from the 79th Scientific Sessions of the American Diabetes Association.

The final morning session of the 79th Scientific Sessions of the American Diabetes Association (ADA) in San Francisco, California, featured more cardiovascular and renal results from recent trials involving type 2 diabetes drugs.

Oral semaglutide, the first glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist in a pill, met safety benchmarks and reduced major cardiovascular (CV) events for high-risk patients with type 2 diabetes (T2D) in PIONEER 6, but did not achieve superiority, according to trial results presented at the 79th Scientific Sessions of the American Diabetes Association in San Francisco, California.

The connections among diabetes, cardiovascular (CV) disease, and kidney failure have been a theme of the 79th Scientific Sessions of the American Diabetes Association, which featured a joint session with the American Society of Nephrology.

The observational study will use information from 3 databases to compare the SGLT2 inhibitor to a competing class of therapy for type 2 diabetes. Early cardiovascular and safety data were presented Monday at the 79th Scientific Sessions of the American Diabetes Association.
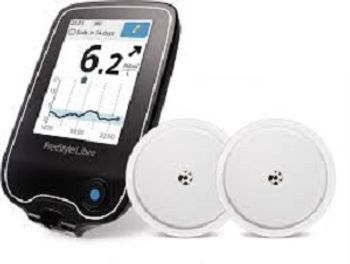
Patients with type 2 diabetes (T2D) who had been using insulin an average of 8 years and had mean glycated hemoglobin (A1C) levels of 8.9% were able to bring their levels down 0.9% after 3 months, according to chart review data from 3 European countries.

Findings reported at the 79th Scientific Session of the American Diabetes Association in San Francisco, California, show the type 2 diabetes drug dapagliflozin significantly reduced the risk of renal decline, kidney failure, and renal death.

Results from a study involving adding sitagliptin and increasing doses of metformin for patients who cannot attain glycemic control show that as glycated hemoglobin increases, it becomes harder to reach targets.

Oral semaglutide would be the first non-injectable agent in the GLP-1 receptor agonist class; these drugs produce powerful glycemic control along with weight loss.
More than 5 years after the full implementation of the Affordable Care Act, outcomes data on the effects of Medicaid expansion are starting to emerge.
The essay appears as 9 states have passed laws that are designed to provoke challenges to Roe v Wade before the Supreme Court of the United States.

The authors, from the CDC, say that while the decline in diabetes incidence occurred alongside public health efforts, it's too soon to assume a causal relationship.

The follow-up to the landmark TAILORx trial shows that adding a clinical risk evaluation of the breast cancer tumor may have prognostic value; the authors' recommendations are drawn from other studies.
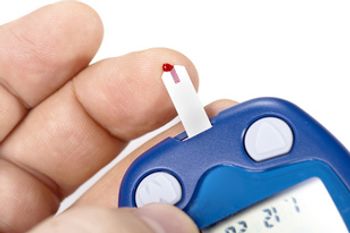
Lack of awareness of hypoglycemia symptoms can be dangerous, because the person with diabetes can experience a dangerous drop in blood sugar; chronic low blood glucose can result in complications.

The analysis showed the opioid cessation rate at 18 months after surgery was 64% among those who used the pain medication before joint replacement, and 95% among those who did not.

This week, the American Psychiatric Association released results of a public opinion survey on several key mental health issues, including how well employees can access mental health care at work.
A well-known brand of blood glucose meters, lancets, and test strips has tapped Sanvita Medical to develop sensors that integrate with its OneTouch Reveal diabetes management app.

259 Prospect Plains Rd, Bldg H
Cranbury, NJ 08512
© 2025 MJH Life Sciences®
All rights reserved.
