Dermatology
Latest News
Latest Videos

More News

Air pollution significantly contributes to and worsens various dermatologic conditions through oxidative stress, inflammation, and disruption of the skin barrier.

There are significant environmental impacts of dermatological practices that call for interdisciplinary collaboration and policy changes to promote sustainability and reduce carbon emissions within the field.

As skin cancer rates continue to rise, here are 5 key facts every health care professional should know to improve prevention, early detection, and patient outcomes.
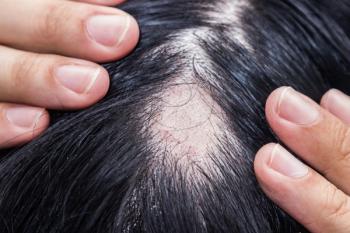
Significant unmet needs were found among high-quality validation studies on the internal structure of patient-reported outcome measures (PROMs) specific to alopecia areata (AA), a common hair loss condition with substantial quality of life impacts.

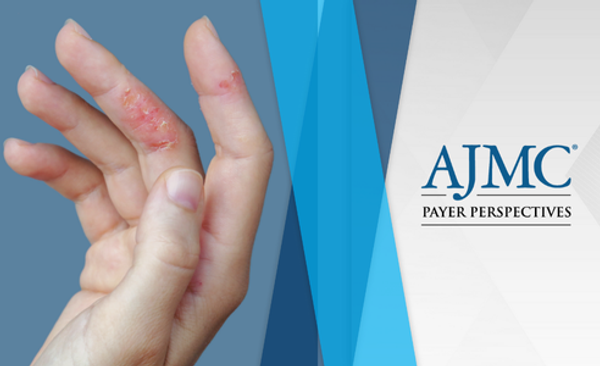
Dermatology providers reported strong impacts on the work and home life of patients with moderate to severe chronic hand eczema, a manifestation of atopic dermatitis.

Raj Chovatiya, MD, PhD, MSCI, highlights the long-term effectiveness of lebrikizumab across diverse patients, including those with prior biologic use, positioning it as a potential first-line treatment for moderate to severe atopic dermatitis.

Raj Chovatiya, MD, PhD, MSCI, highlights promising research in atopic dermatitis focused on identifying patient subgroups for targeted treatments and achieving long-term remission.

US migrant populations experience various dermatologic conditions linked to exposures before, during, and after migration, often exacerbated by barriers to accessing health care.

Research presented at the 2025 Academy of Managed Care Pharmacy annual meeting analyzed real-world treatment outcomes for dermatologic conditions, specifically highlighting the efficacy of ruxolitinib cream for atopic dermatitis and the potential for phototherapy to delay costly biologic initiation.

Crystal Aguh, MD, FAAD, Johns Hopkins School of Medicine faculty, highlights the critical need for comprehensive education on hair loss across diverse hair types, stressing the importance of understanding inflammatory pathways for developing targeted therapies.

Crystal Aguh, MD, FAAD, Johns Hopkins School of Medicine faculty, advocates for increased funding and education to address hair loss disparities within the African diaspora, emphasizing the need for culturally sensitive treatment and research.

Elizabeth Jones, MD, FAAD, highlights the persistent issue of insurance companies favoring expensive, newer medications over equally effective generics in dermatology, emphasizing the time-consuming prior authorization process and advocating for patient partnerships and systemic improvements.

Steven Daniel Daveluy, MD, FAAD, discussed how artificial intelligence (AI) can leverage extensive patient data and guide dermatologists to improve early diagnosis and treatment of rare dermatological diseases through teledermatology.

Elizabeth Jones, MD, FAAD, Thomas Jefferson University Hospitals, highlights the continued relevance of older, generic dermatologic therapies despite the availability of newer, targeted treatments.

In an interview with Brittany Craiglow, MD, FAAD, dermatologist at Dermatology Physicians of Connecticut in Fairfield, she advocates for combination therapies using baricitinib to treat pediatric alopecia areata and highlights the need for personalized treatment approaches based on Janus kinase inhibitor responses.

Lawrence F. Eichenfield, MD, FAAD, from Rady Children's Hospital and UC San Diego School of Medicine, highlighted the effectiveness of ruxolitinib cream as a nonsteroidal topical treatment for atopic dermatitis, its potential to reduce the need for systemic therapies, and the significant role of the skin microbiome in disease management.

Discussions centered on mitigating the financial burden of pediatric atopic dermatitis through financial aid programs and enhancing support for young patients to independently manage their condition were emphasized at this year’s 2025 American Academy of Dermatology meeting.

The clinical and financial implications of inpatient dermatology were examined, highlighting the need for systemic changes to improve care, reduce costs, and address health equity for patients with skin diseases.

Patients with mild atopic dermatitis who reported nighttime scratching experienced relief when they used an artificial intelligence (AI)-powered wearable sensor that delivered haptic feedback on sleep behaviors.

Patients with hidradenitis suppurativa experience knowledge gaps on effective treatments and addressing these gaps could help prevent tissue damage among these patients.

Biosimilar SB17 demonstrated clinical biosimilarity to reference ustekinumab after switching among patients with psoriasis for up to 52 weeks.

Dermocosmetics alongside traditional acne treatments improved skin tolerance and reduced acne severity in patients, particularly those using retinoids, leading to enhanced quality of life.

Increased eczema risks in certain populations were associated with moderately high calcium intake, although pregnant women were found to potentially benefit from higher calcium consumption.
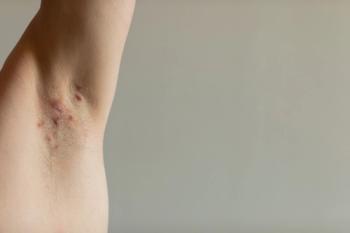
Adalimumab and secukinumab are the only FDA-approved biologic drugs to treat hidradenitis suppurativa, limiting options for patients, especially those who experience loss of response.

For diverse patient populations who are historically marginalized within health care, student-run clinics may offer a potentially cost-effective access point to dermatological care.