Dermatology
Latest News
Latest Videos

More News

Hilary Baldwin, MD, FAAD, highlighted diagnostic complexities and shared treatment strategies for rosacea in patients with darker skin tones at the Skin of Color Update in New York City last Friday.

Valerie M. Harvey, MD, MPH, FAAD, founder of the Hampton Roads Center for Dermatology, highlighted the long-standing underrepresentation of minority populations in dermatology clinical trials at the Skin of Color Update 2024 in New York City on Friday.

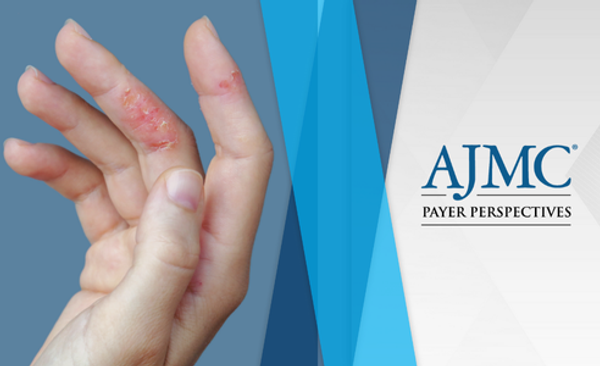
The FDA has approved lebrikizumab (Ebglyss; Eli Lilly) as a new first-line biologic treatment for patients aged 12 and older with moderate to severe atopic dermatitis (AD).
Experts at the Skin of Color Update today in New York City highlighted recent FDA-approved dermatological treatments and emphasized the importance of clinical trial diversity.

Patients With Vitiligo Experience Poorer Quality of Life but Greater Health Care Access, Utilization
Compared with those without vitiligo, patients with vitiligo have higher health care access and utilization but report a lower quality of life.

Kristen Whitney, DO, FAAD, dermatologist within the Allegheny Health Network, discusses advancements in dermoscopy, predicting that emerging technologies and artificial intelligence (AI) will improve dermatologists' efficiency in monitoring and diagnosing skin conditions.

In this discussion, panelists offer their final thoughts.

Patients with vitiligo and psychosocial comorbidities face significantly higher overall health care utilization and costs, although their vitiligo-related expenditures remain similar to those without such comorbidities.

In this discussion, panelists explore the potential role of new Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitors in the treatment landscape for chronic spontaneous urticaria (CSU), evaluating their stages of development and expected impact on treatment algorithms, while also considering future changes in coverage and payer strategies with the emergence of new therapies.

A panel of experts discuss the clinical trials of dupilumab, the resultant data, and the response of the FDA when approval was requested.

The FDA has approved nemolizumab (Nemluvio; Galderma) to treat patients with prurigo nodularis based on successful phase III trials demonstrating significant reductions in itch and sleep disturbances.

Challenges in choosing between corticosteroids and noncorticosteroids for pediatric dermatologic conditions include balancing efficacy, safety, compliance, and long-term management while considering the specific needs and risks of each child.

Steve Feldman, MD, PhD, of Wake Forest University School of Medicine, discusses how adverse event risks influence atopic dermatitis treatment selection and highlights promising new therapies offering effective itch control with minimal side effects.

A panel of experts discuss the key updates needed in CSU guidelines, as they have not been updated since 2014.

Panelists discuss how 30%-50% of patients with chronic spontaneous urticaria remain symptomatic despite treatment, examining the impact of treatment burdens, the limitations of targeting the IgE pathway, and the need for new therapies addressing the IgG pathway.
This new study confirms the noninferiority of extended dosing intervals for psoriasis control in super responders.
Vivian Shi, MD, FAAD, offers clinical insights on best practices for optimizing multidisciplinary care of patients with hidradenitis suppurativa.

Dr. Shi provides insights on patients with hidradenitis suppurativa for whom surgical intervention would be an appropriate treatment modality.

Steve Feldman, MD, PhD, of Wake Forest University School of Medicine, considers dupilumab the "gold standard" for itch control in patients with atopic dermatitis due to its minimal adverse effects.

Posters presented at the Society for Pediatric Dermatology Annual Meeting shed new light on pediatric hair loss, including the rising prevalence of androgenetic alopecia in children, the potential of artificial intelligence to assess hair loss severity, and the long-term safety of ritlecitinib for treating alopecia areata in adolescents.

Steve Feldman, MD, PhD, of Wake Forest University School of Medicine, discusses various effective treatments for alleviating itch in patients with atopic dermatitis (AD), including dupilumab and Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors.
Two posters presented at the Society for Pediatric Dermatology Annual Meeting explored common health conditions linked to childhood alopecia areata and the effectiveness of dupilumab treatment in children with both alopecia areata and atopic dermatitis.

Patients with atopic dermatitis who use oral corticosteroids for more than 90 days have a slightly increased risk of adverse events like myocardial infarction and hyperlipidemia.
The Society for Pediatric Dermatology (SPD) Annual Meeting focused on different aspects of pediatric dermatology, including topical treatments, technology, and misinformation.

A literature review found a link between COVID-19 vaccination and alopecia, with most cases experiencing hair loss within 1 month after the first dose. However, the small sample size and limited data call for further investigation.