Dermatology
Latest News
Latest Videos

CME Content
More News
Vivian Shi, MD, FAAD, provides an overview of current treatment guidelines for hidradenitis suppurativa and discusses ways to improve upon them.

An expert on hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) provides an overview of the Hurley staging system and discusses unmet needs in the overall treatment landscape.
Experts in dermatology presented ways in which biologic therapies can be given and the duration of treatment when used in pediatric patients with skin conditions.
Posters presented at the Society for Pediatric Dermatology Annual Meeting found that pediatric deroofing can lead to patient satisfaction later in life.
Updates in nonsteroidal topical therapies were presented during a session at the Society for Pediatric Dermatology Annual Meeting.

A presentation at the Society for Pediatric Dermatology Annual Conference discussed how to use generative artificial intelligence (AI) to improve processes while working in the dermatology space.

The Society for Pediatric Dermatology (SPD) Annual Meeting featured a new debates segment where experts in the field discussed preferred strategies for the treatment of pediatric skin conditions.

Twice-daily application of 1.5% ruxolitinib cream was found to be effective in children and adolescents with atopic dermatitis and vitiligo.

Today, the FDA approved roflumilast cream 0.15% (Zorvye; Arcutis Biotherapeutics) for the treatment of mild to moderate atopic dermatitis in patients 6 years and older.

Patients with vitiligo have a higher genetic risk of developing rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE).
Iltefat Hamzavi, MD, discusses the importance of support groups and other helpful resources for families and caregivers of patients with hidradenitis suppurativa and provides closing thoughts for clinical providers.

Dr Hamzavi discusses how clinicians can address the psychosocial impact of hidradenitis suppurativa on patients and the rate of hospitalization.

The annual meeting will take place in Toronto July 11-15, 2024.

Iltefat Hamzavi, MD, outlines comorbidities associated with hidradenitis suppurativa and discusses best practices for coordinating care between specialists.

In addition to ensuring residency programs provide educational and practical opportunities for addressing skin of color (SOC) hair-related concerns, prioritizing having residents of diverse backgrounds can help close knowledge and comfort gaps, suggest researchers.

Israeli patients with vitiligo exhibit a significantly reduced risk of developing Parkinson disease (PD).
With an emerging hypothesis that inflammation of the skin prompts intestinal remodeling through various mechanisms, researchers explored the role of inflammatory signals, microbiome alterations, metabolites, and the nervous system.

Researchers have identified a link between psoriasis and the autoimmune diseases hypothyroidism and alopecia areata.

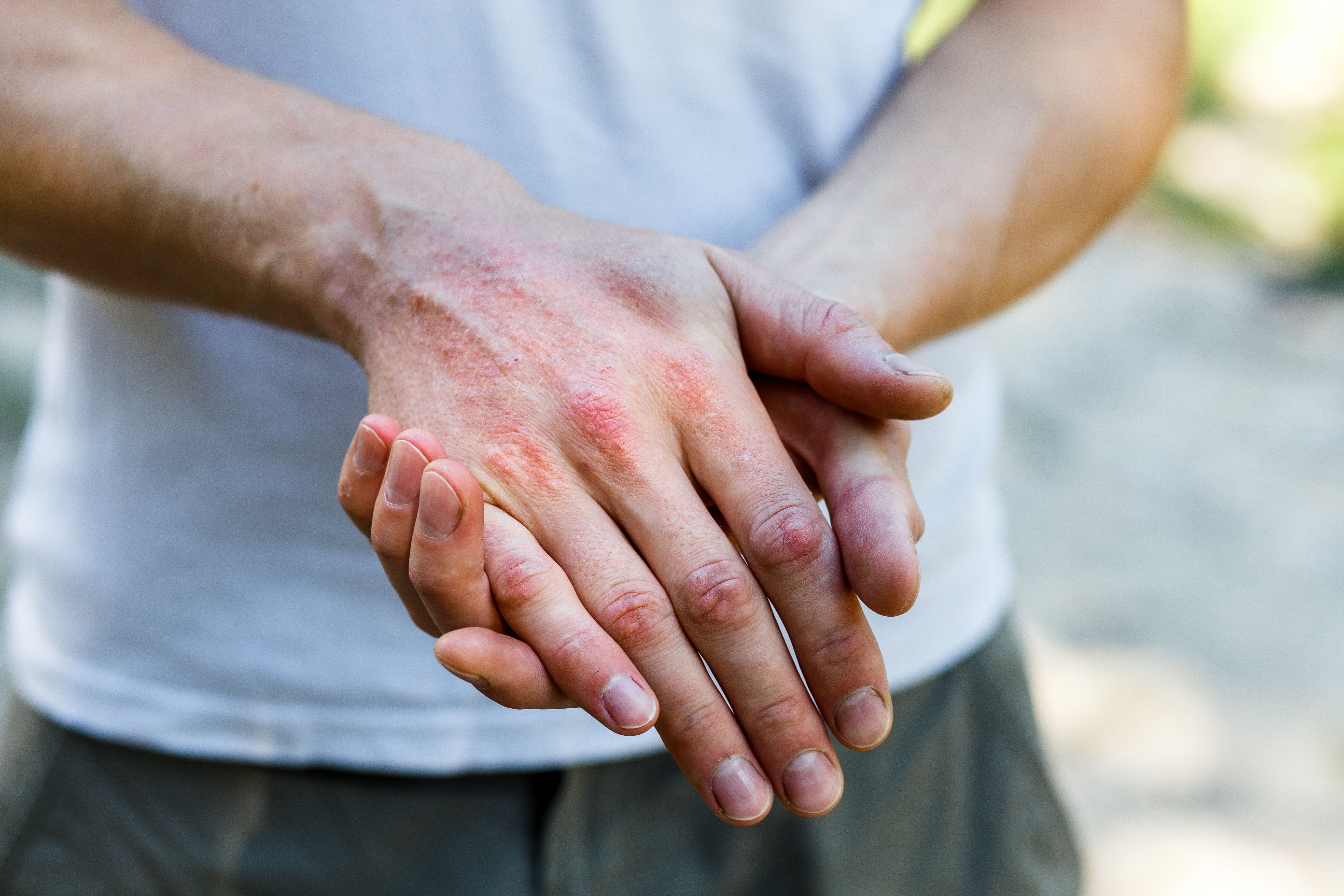
Atopic dermatitis significantly impairs female patients' sexual function, reproductive desires, and overall quality of life.

Excessive dietary sodium intake is linked to increased prevalence and severity of atopic dermatitis (AD).

This week, the Center on Health Equity and Access covered the release of the best US hospitals for equitable access, news from the CMS Health Equity conference, biomarker testing legislation, and insights on improving access for queer communities and the disparities in dermatology.

Shawn Kwatra, MD, dermatologist, John Hopkins University, recounts his study assessing the use of nemolizumab in prurigo nodularis presented at the American Academy of Dermatology conference.

An Italian review highlighted the potential of AI to enhance early diagnosis and treatment of hidradenitis suppurativa, though challenges such as data privacy, algorithm bias, and interpretability must be addressed to fully leverage AI's benefits in dermatology.
A recent study found significant regional disparities and a decline in inpatient dermatology encounters and providers across the US from 2013 to 2019, highlighting the need for increased support and improved access to specialized dermatologic care.

A US-based discrete choice experiment survey found that patients with atopic dermatitis (AD) prioritize treatments that effectively control itching.