Leukemia and Lymphoma
Latest News

Latest Videos
CME Content
More News

Two posters presented at AMCP Nexus 2021 analyzed the costs of treating cytokine release syndrome and neurological events, 2 common adverse events (AEs) of chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy.
Posters presented at AMCP Nexus 2021 evaluated the health care resource utilization (HRU) and costs associated with the chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapies tisagenlecleucel and axicabtagene ciloleucel.

Posters presented at the AMCP Nexus 2021 meeting reviewed the cost-effectiveness and cost per response for zanubrutinib vs ibrutinib.
Investigators in a retrospective study of patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) sought to understand the correlation between muscle loss and immunochemotherapy.

On this episode of Managed Care Cast, we bring you an interview conducted by the editorial director of OncLive® who talks with the advance practice provider chief at Winship Cancer Institute about how having a dedicated cancer urgent care center will make cancer treatment plans seamless whil helping patients avoid exposure to infectious diseases in emergency department waiting rooms.




People who receive organ transplants have an elevated risk of developing cancer, particularly lung cancer and non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL).
There is a lot of evidence on the disparities in cancer care, but less on how to take those findings and turn them into actionable items to address the problem, said Karen Winkfield, MD, PhD, executive director of the Meharry-Vanderbilt Alliance.

A recently published review outlines progress made in discovering biomarkers for chronic myeloid leukemia (CML).

Dosing from pivotal phase 3 trials of tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) in chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) is not optimal for real-world patients who experience different efficacy and adverse events (AEs).
These second-generation inhibitors include acalabrutinib, zanubrutinib, and tirabrutinib, and researchers hope they can overcome the off-target toxicity and treatment resistance that can be experienced with ibrutinib.

Two posters presented at the European Society of Medical Oncology highlighted the unmet needs of cancer survivors.

A review of current data identified areas of progress in Bruton tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibition for patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL).
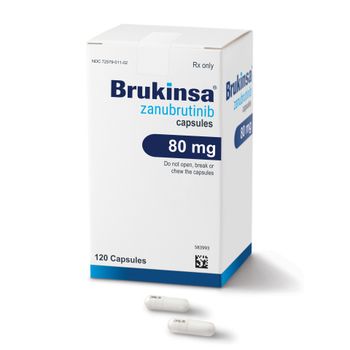
This is the third approval for zanubrutinib, which is sold as Brukinsa by BeiGene.

Two posters being presented at the European Society for Medical Oncology Congress 2021 highlighted the need to provide long-term psychosocial support for adolescents who survive childhood leukemia.
In a recent study, researchers were able to show how different evolutionary forces in aging blood stem cells impact whether or not someone develops acute myeloid leukemia (AML), offering insight into those at higher risk of the disease.

Results of a data analysis found once-daily zanubrutinib dosing in patients with mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) is safe and effective.

Unlike most other cancers, the progression of hairy cell leukemia is largely driven by extended cell survival rather than increased proliferative cell fractions.
Ruxolitinib is increasingly being used in patients with graft-vs-host-disease (GVHD); a recent study found a link with transplant-associated thrombotic microangiopathy (TA-TMA) in patients with GVHD treated with the therapy.

The approval of zanubrutinib makes it just the second therapy indicated for this rare type of lymphoma.
The findings, if confirmed in subsequent research, could prove to have significant implications, as only a small subset of patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) respond to chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy.

The meta-analysis collected findings from 11 studies, from which researchers determined statistical heterogeneity regarding the incidence of GVHD between patients receiving only HSC transplantation or only killer cell therapy, and patients receiving HSC transplantation in addition to killer cell therapy.

A recent study found that older age, male gender, lack of surgical resection or chemotherapy, and late-stage disease may be poor prognostic factors for diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) of the urinary tract.