
Steven R. Feldman, MD, PhD, professor of dermatology, Wake Forest School of Medicine, discusses the challenges clinicians face when managing psoriasis in patients who also have metabolic syndrome.

Steven R. Feldman, MD, PhD, professor of dermatology, Wake Forest School of Medicine, discusses the challenges clinicians face when managing psoriasis in patients who also have metabolic syndrome.
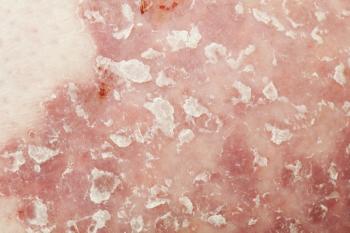
Knowing who may respond to tildrakizumab early on may help providers and patients decide whether to continue with treatment, the researchers said.





Patients with psoriasis who were treated with biologics were less likely to develop psychiatric illnesses compared with patients not treated with biologics; however, the researchers did note treatment selection may have influenced the findings.

Measurement of drug levels early in treatment with ustekinumab for patients with psoriasis may be able to successfully predict patient response and, therefore, direct a treatment strategy.

Psoriasis is known to be linked with metabolic syndrome, which is triggered by chronic inflammation and fosters obesity and dyslipidemia. A recent study looked at another chronic inflammatory skin disease, lichen planus, to better understand any associations with metabolic syndrome.

The discussion about whether existing inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) or new IBD can worsen after secukinumab therapy is not resolved, the researchers said.

Human leukocyte antigen c (HLA‐C), a protein encoded by the HLA-C gene, plays an important role in protecting against both cancer and viruses. At the same time, it has been implicated in autoimmune diseases, including rheumatic diseases, though the mechanism by which it contributes to the pathogenesis of these diseases is not yet clear.

Some patients may use alcohol to cope with the psychological and social aspect of psoriatic disease, but using alcohol may be associated with worse adherence to treatment.
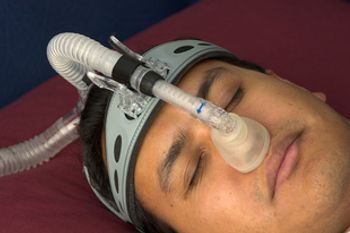
Patients with psoriasis should be opportunistically screened for obstructive sleep apnea, an independent risk factor for cardiovascular disease, said the authors of a recent study.
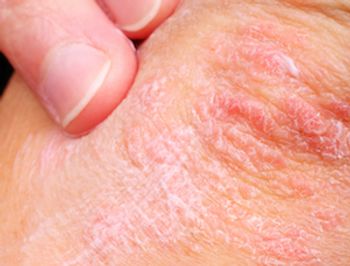
August is National Psoriasis Month, which aims to raise awareness about this chronic autoimmune disease affecting more than 8 million Americans. Here are 5 things to know about psoriasis and its complications.
The National Psoriasis Foundation is working to get laws to curb to step therapy practices at the state level.

The price for Otezla is higher than many analysts expected.
Findings appeared this month in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology.

Biologics have become the standard of care for rheumatoid arthritis (RA) that fails to respond adequately to conventional disease-modifying antirheumatic agents (DMARDs), and overall, these agents are safe and effective. However, an association between treatment with anti–tumor necrosis factor (anti-TNF) agents and new-onset psoriasis in patients with RA has been observed.
A psoriasis researcher discusses a new class of psoriasis treatments.
“Our data suggest that people with central obesity, insulin resistance, and active psoriasis are the most at risk for liver fibrosis,” wrote the authors, and “if use of methotrexate is a risk factor, it is not the only risk factor and for most patients it is unlikely to be the most important risk factor.”

A recent review of biomarkers of subclinical atherosclerosis in patients with psoriatic arthritis (PsA) showed more severe atherosclerotic disease compared with patients who have only psoriasis.

During a recent meeting of the British Association of Dermatologists, a team of researchers from the United Kingdom reported on a systematic review of literature on adults exposed to biologics during conception and/or pregnancy, and they report that they did not find increased risk to the fetus following maternal or paternal biologic exposure.
Biologic treatment for moderate to severe psoriasis was linked with reduced coronary inflammation as determined by a new imaging biomarker, according to a study published in JAMA Cardiology.
In a study presented at the British Association of Dermatologists’ 99th Annual Meeting in Liverpool, United Kingdom, July 2-4, 2019, researchers from the University of Manchester and the Salford Royal National Health Service Foundation Trust reported on an effort to assess evidence on the risk of cancer in patients with psoriasis. They found that there are a number of site-specific cancers for which patients with psoriasis are at elevated risk.

Therapeutic drug monitoring that includes the measurement of trough concentrations and anti-drug antibodies, along with clinical response, is a tool for clinical decision making.

259 Prospect Plains Rd, Bldg H
Cranbury, NJ 08512
© 2025 MJH Life Sciences®
All rights reserved.
