Technology
Latest News
Latest Videos

CME Content
More News

The 10th annual health IT special issue of The American Journal of Managed Care® captures the opportunities and disparities that have emerged after telehealth broke through the barriers that kept it out of reach.

Setting up a new tool to capture electronic patient-reported outcomes (ePROs) requires a lot of prep work to ensure patients are comfortable and ready to use the tool, said Amy Ellis, chief quality officer at Northwest Medical Specialties.

A letter from the guest editor highlights the contributions of health information technology in improving health care delivery patient-centeredness through innovation in data analytics, connecting providers, and implementation of telehealth.

Natural language processing can be used for automated extraction of social work interventions from electronic health records, thereby supporting social work staffing and resource allocation decisions.

Results of a vignette-based survey study indicate patients with diabetes require greater health benefits to adopt more intrusive remote digital monitoring (RDM), food monitoring, and real-time feedback by a health care professional.

Deep learning algorithms could improve palliative care by predicting mortality from electronic health records and claims data.
Adapting to telehealth was not difficult, but practice transformation around telehealth has been more difficult, and there remains the future uncertainty around continued reimbursement, said Sibel Blau, MD, of Northwest Medical Specialties and Quality Cancer Care Alliance.

Patients’ access to and use of online medical records (OMRs) can facilitate better management of their health care needs; however, disparities persist. This study highlights the disparities among individuals’ OMR use and why individuals who are offered OMRs do not use them.

This study evaluates the growth in electronic consultation use over the first 7 years after its implementation across the entire Veterans Health Administration system.

This retrospective cohort evaluation found that patients receiving electronic, compared with face-to-face, specialty consultation had significantly lower health care costs for at least 3 months.

During the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic, we found lower use of video vs telephone visits among older, Black, Hispanic, and Spanish-speaking patients, driven largely by clinician and practice factors.

Direct access of primary care physicians to dermatologists via asynchronous teledermatology improves a health system’s ability to increase patient access to dermatologic care.

The telehealth policy changes enacted for short-term control of the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic present an opportunity to address the fundamental gap in health care underutilization.

TeleConnect introduces the concept of connecting primary care physicians and specialists by leveraging technology. Improving communication in a health care system betters patient care.

With a rapid shift to telehealth during the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic, clinicians, health care organizations, and policy makers must consider and address patients’ evolving needs, concerns, and expectations.

Deep Learning Model Detects Sea Fan Neovascularization in Patients With Sickle Cell Hemoglobinopathy
In an effort to detect sea fan neovascularization from ultra-widefield color fundus photographs from patients with sickle cell hemoglobinopathy, researchers developed an automated system with high sensitivity and specificity, which holds potential to improve screening for vision-threatening proliferative sickle cell retinopathy.

Recent major investments signal growth in an emerging therapeutic sector.

Texas Oncology physicians discuss utilization of telemedicine, evaluating trends, barriers, and opportunities in care delivery during the coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic.
Stark realities exposed by the pandemic have led some to advocate for redirecting resources to have the most impact on vulnerable populations.

What people believe about health and public health, although challenged before the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic, is even more crucial now as vaccine distribution efforts could soon begin.

Researchers found the application of FOLFOXai, an artificial intelligence (AI)–based predictor of response to FOLFOX chemotherapy in metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC), may lead to improved treatment outcomes for some patients with mCRC and other cancers.

Using machine learning methods researchers were able to extract records of patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) from electronic health record data with high precision, enabling research on very large populations with this condition for limited costs.

Large telemedicine diabetic retinopathy screening networks based in federally designated safety-net clinics may be able to increase screening access and compliance among otherwise underscreened populations.
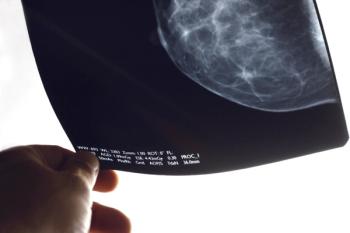
Supplemental screening for breast cancer, beyond the standard-of-care mammography, may benefit some women who have dense breast tissue.

Artificial intelligence (AI) frees up time for clinicians, noted Anthony L. Loschner, MD, assistant professor and associate program director, Critical Care Fellowship Program, Virginia Tech Carilion School of Medicine.