
A review explored the potential role of eosinophils and their mediators in the pathophysiology of chronic rhinosinusitis (CRS) subtypes.


A review explored the potential role of eosinophils and their mediators in the pathophysiology of chronic rhinosinusitis (CRS) subtypes.

Matthew J. Zirwas, MD, a dermatologist in Ohio, discusses how dermatologists may stratify patients with atopic dermatitis (AD) with the launch of new biologic treatments in 2021.

The review of 32 studies revealed that biologic treatment tended to favor patients with allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis (ABPA) and asthma rather than those with cystic fibrosis (CF).

In addition to significant morbidity and impaired health-related quality of life, patients with atopic dermatitis have a significant out-of-pocket (OOP) financial burden related to their disease.

This year, the most popular articles and interviews related to the role of inflammation in asthma and other conditions touched on the mechanisms of inflammation, patterns of inhaler use, and the real-world impacts of the monoclonal antibody dupilumab.

The analysis reviewed the safety and efficacy among patients in Japan to confirm the findings of the overall study population.

The treatment landscape for atopic dermatitis is beginning to change from the use of topical therapies to biologics and more, said David Pariser, MD, senior physician at Pariser Dermatology Specialists and professor at Eastern Virginia Medical School Department of Dermatology.

Older adults are often at greater risk for adverse events from treatments, but they can also be excluded from randomized controlled trials (RCTs), making it difficult to know if findings are generalizable to this population.

This article describes food allergy–related service utilization and identifies factors associated with guideline-informed care among Medicaid-enrolled US children with food allergy.

Investigators concluded that use of a new registry could aid in the recruitment of pediatric subjects with severe asthma and the design of future clinical trials for emerging biologics.

The comorbidities associated with atopic dermatitis can be substantial, and the disease can have a significant burden on quality of life, but new biologics and other future treatments may help, said David Pariser, MD, senior physician at Pariser Dermatology Specialists.

The financial, physical, and social burdens of atopic dermatitis can be substantial, especially for patients who had the condition as children into adulthood, said David Pariser, MD, senior physician at Pariser Dermatology Specialists and professor at Eastern Virginia Medical School Department of Dermatology.

Updated guidance in 6 key areas of asthma care focus on improving diagnosis, management, and treatment.

As the only biologic on the market, dupilumab has replaced most of the more traditional treatments for atopic dermatitis, said David Pariser, MD, senior physician at Pariser Dermatology Specialists.

Patients with asthma can improve their disease control and sleep quality, while reducing depression and anxiety through a behavior change intervention aimed at increasing their physical activity.

Expansion of insurance coverage due to the Affordable Care Act led to a reduction in the use of emergency services for patients with asthma in New York City.
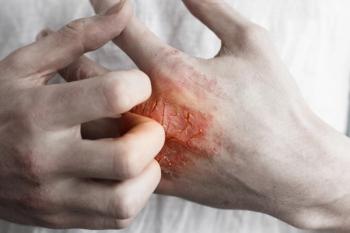
Dupilumab, with or without topical corticosteroids, significantly reduced pain and discomfort in patients with moderate to severe atopic dermatitis.

Treatment targets include several interleukins, immunoglobulin E, and alarmins, pointed out Nicola Hanania, MD, MS, pulmonary critical care physician and director, Airway Clinical Research Center, Baylor College of Medicine, Houston.

Overuse of reliever inhalers among adult patients with asthma is prevalent, but does not necessarily translate into higher all-cause health care utilization (HCU), according to a study published in Scientific Reports.

Categorizing by eosinophilic/noneosinophilic subtype enables better targeted treatment, noted Anne Reihman, MD, third-year pulmonary and critical care fellow, University of Colorado, Division of Pulmonary Sciences and Critical Care Medicine.

Vitamin D used as an adjuvant therapy in children with severe atopic dermatitis may improve clinical outcomes, according to a recent study.

Despite the price, adherence to biologics for asthma is usually good because of the effectiveness, said J. Allen Meadows, MD, president of the American College of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology.

When the first biologic to treat asthma was approved by the FDA in 2003, it needed to be administered subcutaneously in the physician’s office. Now, there are 3 options available for at-home use: mepolizumab, benralizumab, and dupilumab.

There are clear differences between the biologics approved to treat asthma, and finding the right one for a patient requires shared decision-making conversations, said J. Allen Meadows, MD.

Atopic dermatitis (AD) has a negative impact on quality of life, and the burden of this disease in adolescents and their parents should be taken into account as part of the management of AD.

259 Prospect Plains Rd, Bldg H
Cranbury, NJ 08512
© 2025 MJH Life Sciences®
All rights reserved.
