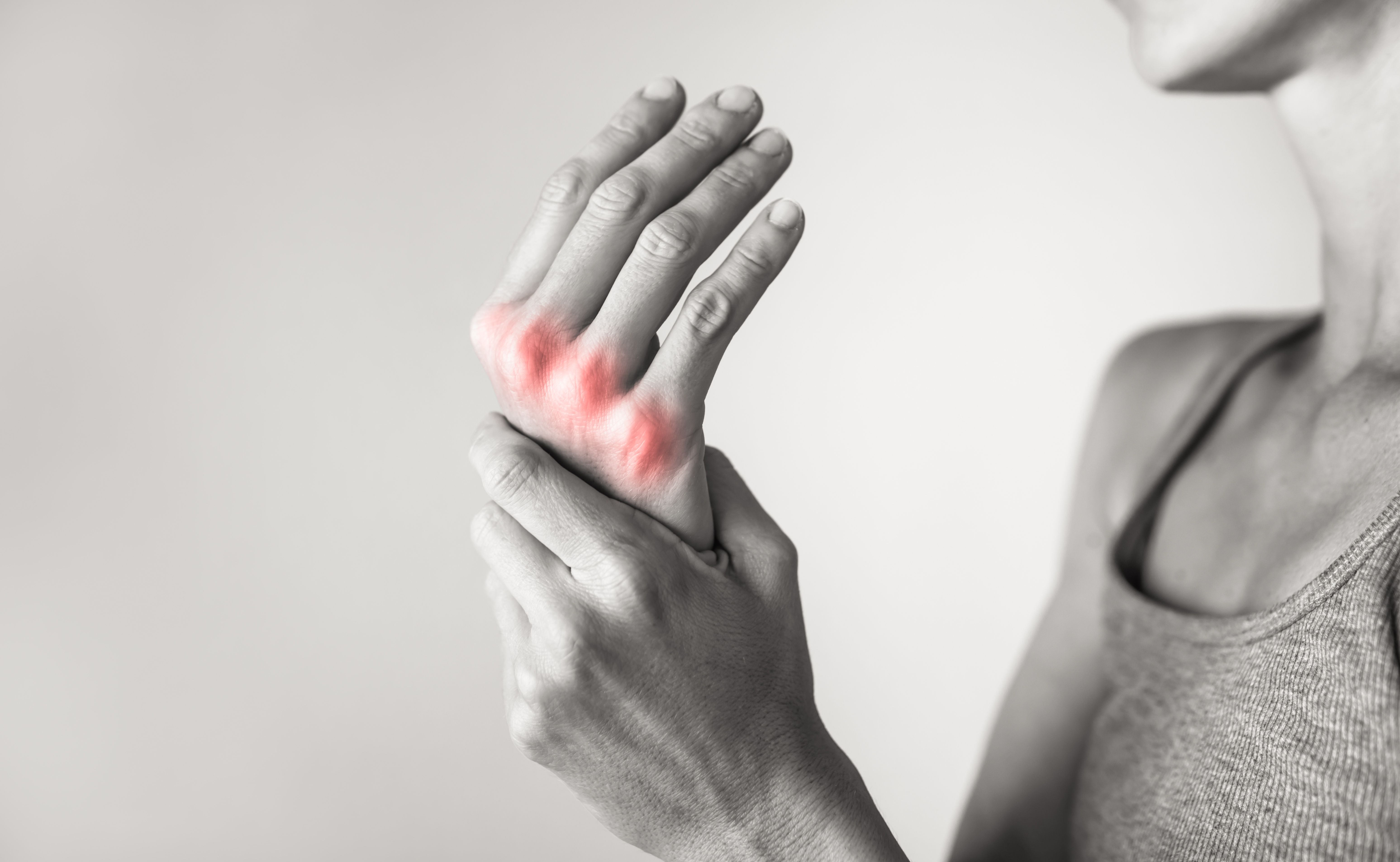
Inflammation
Latest News
Latest Videos

More News

Following the FDA approval of vonoprazan in the treatment of erosive esophagitis, Dr Colin Howden discussed important information about the new therapy.
This data represented the first-ever research presented at ACR on both fractures and calcium pyrophosphate deposition disease.

A cross-sectional study revealed that neuroinflammation is linked to irritability, among other neuropsychiatric symptoms, in patients with Alzheimer disease (AD).

Raj Chovatiya, MD, PhD, assistant professor of dermatology at Northwestern University's Feinberg School of Medicine, discussed type 2 inflammation in atopic dermatitis, prurigo nodularis, and chronic spontaneous urticaria.

In a real-world, prospective study, upadacitinib demonstrated great potential for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) regardless of a patient’s baseline C-reactive protein (CRP) levels.

New data show one-quarter of patients with kidney disease associated with IBD progress to end-stage disease, with primary determinants including age and baseline eGFR.
Results showed higher-exposure dupilumab met the study’s primary endpoint for peak esophageal intraepithelial count ≤6 eos/high-power field.

Posters presented at the American College of Gastroenterology's (ACG's) 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting examined potential environmental risks of eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) on the pediatric population, as well as the presence of allergic comorbidities in children diagnosed with EoE.


A co-expression network analysis pinpoints different gene expressions that can potentially predict rheumatoid arthritis (RA) outcomes during pregnancy.
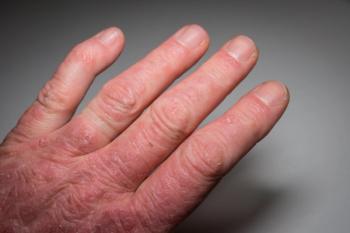
A study from UCSD highlights how advances in imaging modalities and utilization could aid in the early detection of psoriatic arthritis.

If approved, the treatment would be the first of its kind for young children enduring eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE).
Persistent disability and risks of death were associated with inflammatory levels in patients following major abdominal surgery.

Patients with IBD-RA and depression were younger, more likely to be female, and were more frequently White compared with controls.
In a longitudinal case study, researchers found that higher inflammation levels may predict poor outcomes following bariatric surgery.
Adverse effects associated with glucocorticoid use among patients with rheumatoid arthritis may not be as burdensome as previously indicated.

Combination endoscopic sinus surgery (ESS) and biological therapy significantly decreased polyp burden in refractory chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyposis (CRSwNP) compared with biologic therapy alone

Through a series of regression analyses, researchers projected the ever-increasing global burden of osteoarthritis (OA) until 2050.
Researchers analyzed numerous biomarkers in patients at risk for inflammatory arthritis to develop measurable scores indicating a patient's vulnerability to disease progression.

New research suggests that measuring the inflammatory marker myeloperoxidase (MPO) may be an effective strategy for the prediction of patients' risk of mortality in a myriad of cardiac—and potentially non-cardiac—diseases.

With data on side-opening cutting forceps showing above a 90% diagnostic rate for tissue biopsy in adult patients with eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) who undergo biopsy of the esophageal lamina propia (ELP), investigators conducted a pilot study on use of side-opening cutting forceps in younger patients.

A study from China suggests calcium and magnesium malnutrition is associated with Crohn's disease inflammation and activity.
The current literature is lacking on outcomes among patients with comorbid chronic rhinosinusitis (CRS) and immunoglobulin deficiencies, especially for those who must use surgery to manage their CRS.
With this study, investigators hoped to advance their understanding of cellulitis-mimicking reactions among patients currently receiving chemotherapy.

Few validated measures exist to quantify sleep disturbance among patients who have the chronic inflammatory skin condition prurigo nodularis.