
In the real world, dupilumab has been as effective as the results in clinical trials, and patients are seeing low exacerbation rates, emergency department visits, and hospitalizations, explained Neal Jain, MD, FAAP, FAAAAI.


In the real world, dupilumab has been as effective as the results in clinical trials, and patients are seeing low exacerbation rates, emergency department visits, and hospitalizations, explained Neal Jain, MD, FAAP, FAAAAI.

Following the onset of the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic, changes in pediatric asthma health care delivery patterns resulted in reduced hospital admissions and systemic steroid prescriptions in Philadelphia.

The 2-year study will investigate how devices like the Apple Watch and the iPhone can help patients with asthma better manage their condition.

Patients who have oral corticosteroid–dependent asthma are recommended to use dupilumab, which reduces the use of oral steroids, explained Neal Jain, MD, FAAP, FAAAAI, of Arizona Allergy & Immunology Research.
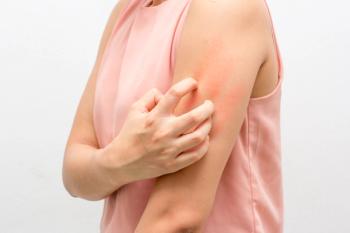
The high rate of persistence found in the real-world study indicates dupilumab was well tolerated and patients were satisfied with its effectiveness.
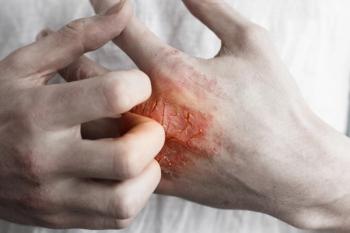
The broadest real-life study of dupilumab in atopic dermatitis (AD) found significant improvements in adults with moderate to severe AD that were even greater than the results reported in clinical trials.

Even though dupilumab was a late entrant to the market to treat asthma, its efficacy “speaks for itself,” said Neal Jain MD, FAAP, FAAAAI, of Arizona Allergy & Immunology Research, Arcadia Allergy & Asthma, and San Tan Allergy & Asthma.

Findings from a new study in JAMA do not support the use of vitamin D3 supplementation to prevent severe asthma exacerbations in children with persistent asthma.

Inflammatory skin diseases are often diagnosed by "first impression" and can be easily misdiagnosed. A new smartphone app using artificial intelligence (AI) may be able to assist with the diagnosis of psoriasis, atopic dermatitis, and eczema.

Acute stress was found to be a possible trigger following the loss of a partner, but not a factor in long-term risk for either disorder.

The aim of this study was to assess cytokine levels in patients with refractory chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps and to identify inflammatory markers associated with certain subtypes.

Results from 2 large clinical trials show that dupilumab is associated with clinical improvements in symptoms of chronic rhinosinusitis (CRS) with nasal polyps.
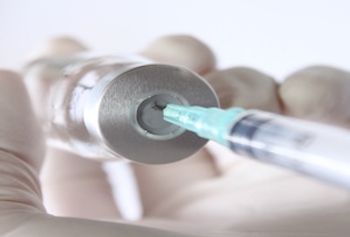
Results of a subgroup analysis within a randomized, controlled trial show that the monoclonal antibody dupilumab (Dupixent) improved clinical and patient-reported outcomes among patients with chronic rhinosinusitis (CRS) with nasal polyps and comorbid asthma.













259 Prospect Plains Rd, Bldg H
Cranbury, NJ 08512
© 2025 MJH Life Sciences®
All rights reserved.
