Inflammation
Latest News
Latest Videos

CME Content
More News

This study was prompted by recent findings that ultra-low IgE levels (IgE <2.5 kU/L) may be linked with a higher risk of cancers.

The most-viewed eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) content of the year covered new developments in treatment options for EoE, the prevalence of EoE in the allergic disease population, and the impact of EoE on a child’s well-being.

This new study, which followed patients up to 6 months after functional endoscopic sinus surgery, evaluated results using objective and subjective measures.
Though a large proportion of patients receiving oral immunotherapy (OIT) for food allergy report gastrointestinal (GI) symptoms, a knowledge gap remains for the best approach to determine the underlying etiology and manage symptoms.

Based on their retrospective findings, the researchers suggest the diet is a potentially effective option for these patients who may face challenges with other elimination diets.
Patients with asthma who were with or without a diagnosis of nasal polyps were found to have results with long-term dupilumab.

The investigators of this study compared outcomes between patients who had eosinophilic or noneosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps (CRSwNP) by comparing the influence of body mass index (BMI) on each disease subtype.

Researchers investigated subgroups of patients with chronic rhinosinusitis with polyposis (CRSwNP), wanting more data on their responses to dupilumab and hoping to stratify their level of benefit.
The findings mean that scarring in the esophagus as a result of eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) can be found earlier, allowing for more targeted intervention.

This new study explored how expression of SERPINB10 may be related to postoperative recurrence of and inflammation related to chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps (CRSwNP).
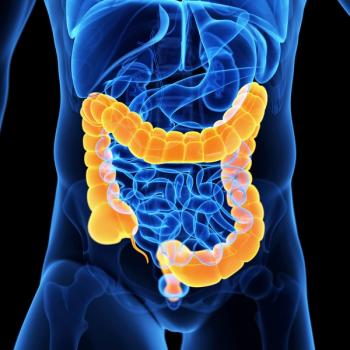
An article published in the journal Gastroenterology & Hepatology highlights recent updates to eosinophilic gastrointestinal disease nomenclature, as well as updates related to diagnosis, pathogenesis, and treatment standards.
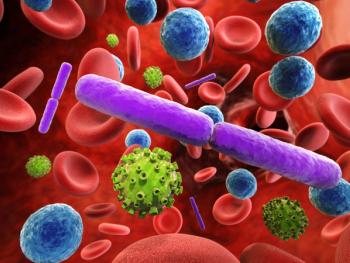
The study findings suggest that eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE), like other atopic diseases, may be associated with infections.

The investigators of this new study wanted to more clearly define the patient characteristics of the 2 main types of chronic rhinosinusitis: with nasal polyps (CRSwNP) and without nasal polyps (CRSsNP).

The investigators of a new study evaluated if nasal cytology was a reliable method to identify type 2 inflammation in patients who have chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps (CRSwNP), which could then facilitate patient selection for biological drug utilization via endotypization.
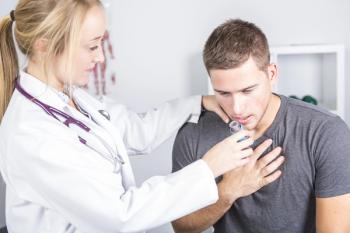
A significant uptick in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps (CRSwNP) among patients with comorbid asthma has been seen in the country over the past decade.
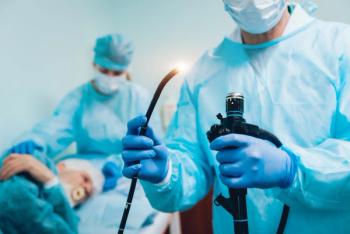
The findings follow recent data suggesting that esophageal dysmotility may be associated with eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE), which often presents with dysphagia.

The study, say researchers, adds insight into risk factors predictive of response to dietary intervention for eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE), as dietary failure occurs in up to 30% of patients.

The index for eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) was crafted based on a literature review by a multidisciplinary team of experts.
The goal of this new study was to gain more information on the disease burden, including costs, of patients living with chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps (CRSwNP).
While the prevalence of eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) is estimated to be 0.5% in the general population, a recent study found that the prevalence was as high as 16.5% in patients with allergic disease.

A search of the peer-reviewed literature turned up inconsistent findings on the effectiveness of corticosteroid irrigation for the treatment of chronic rhinosinusitis (CRS) with nasal polyps.

The effect of dupilumab was investigated among patients with severe and uncontrolled chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps (CRSwNP).

Despite extensive study, eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis (ECRS) remains a significant health problem with few effective treatments, so this study compared periostin levels among those who did and did not have ECRS to assess its potential as a disease biomarker.

Researchers investigated potential risk factors for the higher occurrence of asthma among individuals who have chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps (CRSwNP).
Overall, 65% of patients went into remission throughout the observation period, with those with concurrent eczema and pollen food syndrome (PFS) having favorable responses.