
Improved outcomes associated with fidaxomicin compared with vancomycin suggest benefits from its greater use in Medicare patients, although uptake remains low despite its recommended use.


Improved outcomes associated with fidaxomicin compared with vancomycin suggest benefits from its greater use in Medicare patients, although uptake remains low despite its recommended use.

CDC's latest Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report showed that US adults of non-Hispanic Black, American Indian or Alaska Native, and Hispanic race/ethnicity exhibited significantly higher influenza hospitalization rates and lower vaccination coverage compared with White adults.

Compared with Ethiopia’s current nonmandatory hepatitis B vaccination program, expanded vaccination coverage among health care workers was shown to be more cost-effective and result in improved life expectancy gains.

Patients with hepatitis C virus infection and chronic homelessness who were placed into permanent supportive housing exhibited a significantly reduced risk of hospitalization and liver-related morbidity and mortality.

Children with acute infective conjunctivitis experienced significantly reduced duration of conjunctival symptoms when treated with topical antibiotics.

Optum and Change Healthcare have completed their merger initiated in 2021; efficacy of the Jynneos vaccine is in question after 90 of 7339 individuals contracted monkeypox after vaccination; the CDC will no longer maintain a list of country-by-country COVID-19 travel advisories.

An FDA advisory committee recently issued a positive vote for Ferring’s RBX2660, an investigational microbiota-based live biotherapeutic, for its potential in reducing recurrent Clostridioides difficile infection after antibiotic treatment.
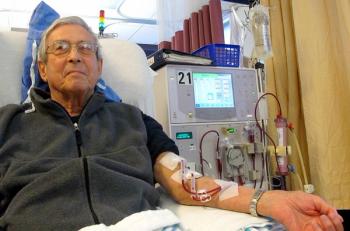
Patients requiring maintenance hemodialysis (MHD) had a 4-fold higher risk of Clostridioides difficile infection (CDI), with rates of CDI increasing over time regardless of MHD requirement.

Rare presentations of encephalitis and transverse myelitis are among neurologic consequences linked with orthopoxviruses of smallpox and monkeypox.

Health experts warn that all should brace for a flu season that could be worse than the past 2 years; the CDC is opening applications to a vaccine equity program that will help those who may have limited access to the monkeypox vaccine; a new report found that health care services will be greatly affected by climate change.

Simply adding an admission screening question and a 2-step testing algorithm sharply decreased the number of Clostridioides difficile infections (CDI) in the year after implementing the interventions.

President Joe Biden is set to sign an order to boost biotech as part of his Cancer Moonshot; the health care program for 9/11 survivors and first responders is running short on money; tecovirimat (Tpoxx) has been found to be safe in patients with monkeypox.
David E. Koren, PharmD, MPH, BCPS, AAHIVP, FIDSA, infectious disease clinical pharmacist at Temple University Hospital, provides an update on current preventive efforts to address the monkeypox public health emergency in the United States and what steps are needed to protect at-risk populations.

A 16% lower adjusted risk in recurrent Clostridioides difficile infections was found in 2018 compared with 2013 across diverse US sites part of the CDC’s Emerging Infections Program.

David E. Koren, PharmD, MPH, BCPS, AAHIVP, FIDSA, infectious disease clinical pharmacist at Temple University Hospital, discussed the risk posed by monkeypox among immunocompromised individuals and men who have sex with men, as well as the need for educational efforts to address misconceptions tied to the disease.

David E. Koren, PharmD, MPH, BCPS, AAHIVP, FIDSA, infectious disease clinical pharmacist at Temple University Hospital, speaks on gaps in monkeypox vaccine availability and access and steps to improve response to the public health emergency.

Anthony Fauci, MD, announced Monday he is stepping down in December 2022 from his various positions, including as head of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, “to pursue the next chapter of my career” and that he is not retiring.
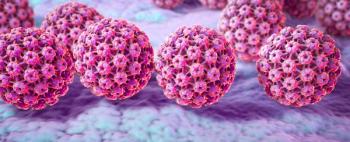
A cross-sectional study found that human papillomavirus (HPV) had a higher probability of being diagnosed in women born in the 1980s compared with women born in the 1990s.

The CDC announced it would be loosening recommendations to battle COVID-19 to put more responsibilities on individuals; Mount Sinai Health System has started building a database of patient genetic information; parts of the country see racial disparities in individuals contracting monkeypox.

Acadia Pharmaceuticals’ pimavanserin (Nuplazid) was not extended by the FDA to include Alzheimer-related psychosis; HHS/Health Resources and Service Administration vow to strengthen rural health care; a new deal has the United States paying $26 million for Siga Technologies’ Tpoxx.

Treatment of hepatitis C virus (HCV) with direct-acting antiviral medications was associated with low HCV reinfection rates among patients who inject drugs, although risk for reinfection was highest in the first 24 weeks of treatment and among those with ongoing injecting drug use.

US cases of monkeypox have risen to 6600, and Thursday's declaration aims to provide enhanced testing, treatment, and vaccine capabilities nationwide.

Proton pump inhibitor use was cited as the only avoidable risk factor for mortality in patients with Clostridioides difficile infection.

The number of monkeypox cases in the United States is close to 3600, the CDC said this week, and on Wednesday, HHS approved a supplement to the biologics license for a vaccine made by Bavarian Nordic to prevent smallpox and monkeypox.

Each additional hour of care per day provided by registered nurses to Medicare beneficiaries admitted to an acute care hospital with a sepsis diagnosis was associated with a 3% decreased risk of 60-day mortality.

259 Prospect Plains Rd, Bldg H
Cranbury, NJ 08512
© 2025 MJH Life Sciences®
All rights reserved.
